healthyverse_tsa
Time Series Analysis and Nested Modeling of the Healthyverse Packages
Steven P. Sanderson II, MPH - Date: 11 July, 2025
This analysis follows a Nested Modeltime Workflow.
Get Data
glimpse(downloads_tbl)
## Rows: 145,104
## Columns: 11
## $ date <date> 2020-11-23, 2020-11-23, 2020-11-23, 2020-11-23, 2020-11-23,…
## $ time <Period> 15H 36M 55S, 11H 26M 39S, 23H 34M 44S, 18H 39M 32S, 9H 0M…
## $ date_time <dttm> 2020-11-23 15:36:55, 2020-11-23 11:26:39, 2020-11-23 23:34:…
## $ size <int> 4858294, 4858294, 4858301, 4858295, 361, 4863722, 4864794, 4…
## $ r_version <chr> NA, "4.0.3", "3.5.3", "3.5.2", NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, N…
## $ r_arch <chr> NA, "x86_64", "x86_64", "x86_64", NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, NA…
## $ r_os <chr> NA, "mingw32", "mingw32", "linux-gnu", NA, NA, NA, NA, NA, N…
## $ package <chr> "healthyR.data", "healthyR.data", "healthyR.data", "healthyR…
## $ version <chr> "1.0.0", "1.0.0", "1.0.0", "1.0.0", "1.0.0", "1.0.0", "1.0.0…
## $ country <chr> "US", "US", "US", "GB", "US", "US", "DE", "HK", "JP", "US", …
## $ ip_id <int> 2069, 2804, 78827, 27595, 90474, 90474, 42435, 74, 7655, 638…
The last day in the data set is 2025-07-09 23:39:04, the file was birthed on: 2022-07-02 23:58:17.511888, and at report knit time is -2.646768^{4} hours old. Happy analyzing!
Now that we have our data lets take a look at it using the skimr
package.
skim(downloads_tbl)
| Name | downloads_tbl |
| Number of rows | 145104 |
| Number of columns | 11 |
| _______________________ | |
| Column type frequency: | |
| character | 6 |
| Date | 1 |
| numeric | 2 |
| POSIXct | 1 |
| Timespan | 1 |
| ________________________ | |
| Group variables | None |
Data summary
Variable type: character
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | empty | n_unique | whitespace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r_version | 104922 | 0.28 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 48 | 0 |
| r_arch | 104922 | 0.28 | 3 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| r_os | 104922 | 0.28 | 7 | 15 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| package | 0 | 1.00 | 7 | 13 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| version | 0 | 1.00 | 5 | 17 | 0 | 60 | 0 |
| country | 12247 | 0.92 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 163 | 0 |
Variable type: Date
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | median | n_unique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| date | 0 | 1 | 2020-11-23 | 2025-07-09 | 2023-07-19 | 1690 |
Variable type: numeric
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | mean | sd | p0 | p25 | p50 | p75 | p100 | hist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| size | 0 | 1 | 1131445.94 | 1512974.6 | 355 | 14701 | 293163 | 2367674 | 5677952 | ▇▁▂▁▁ |
| ip_id | 0 | 1 | 10467.59 | 18596.7 | 1 | 288 | 3039 | 11844 | 209747 | ▇▁▁▁▁ |
Variable type: POSIXct
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | median | n_unique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| date_time | 0 | 1 | 2020-11-23 09:00:41 | 2025-07-09 23:39:04 | 2023-07-19 19:35:34 | 89148 |
Variable type: Timespan
| skim_variable | n_missing | complete_rate | min | max | median | n_unique |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| time | 0 | 1 | 0 | 59 | 8 | 60 |
We can see that the following columns are missing a lot of data and for
us are most likely not useful anyways, so we will drop them
c(r_version, r_arch, r_os)
Plots
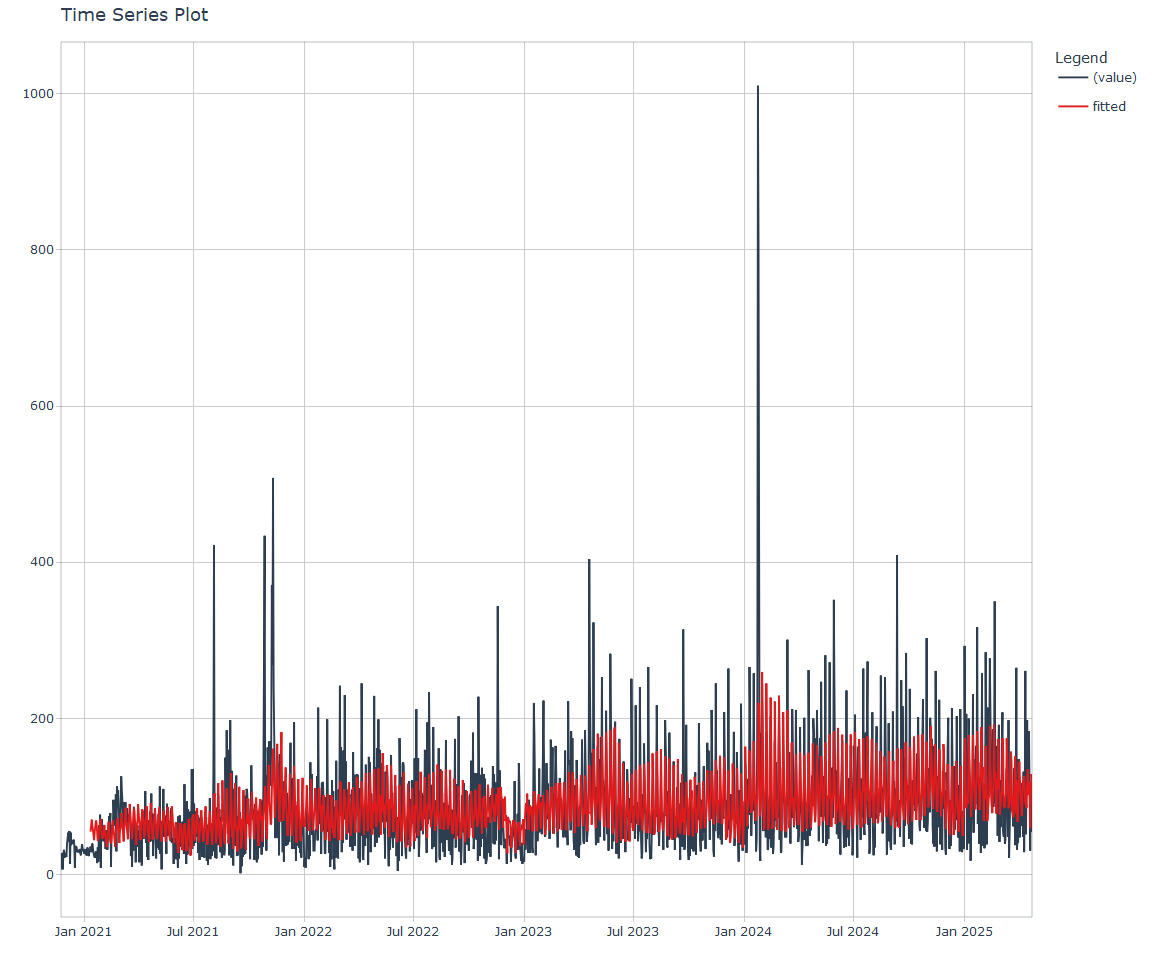
Now lets take a look at a time-series plot of the total daily downloads by package. We will use a log scale and place a vertical line at each version release for each package.
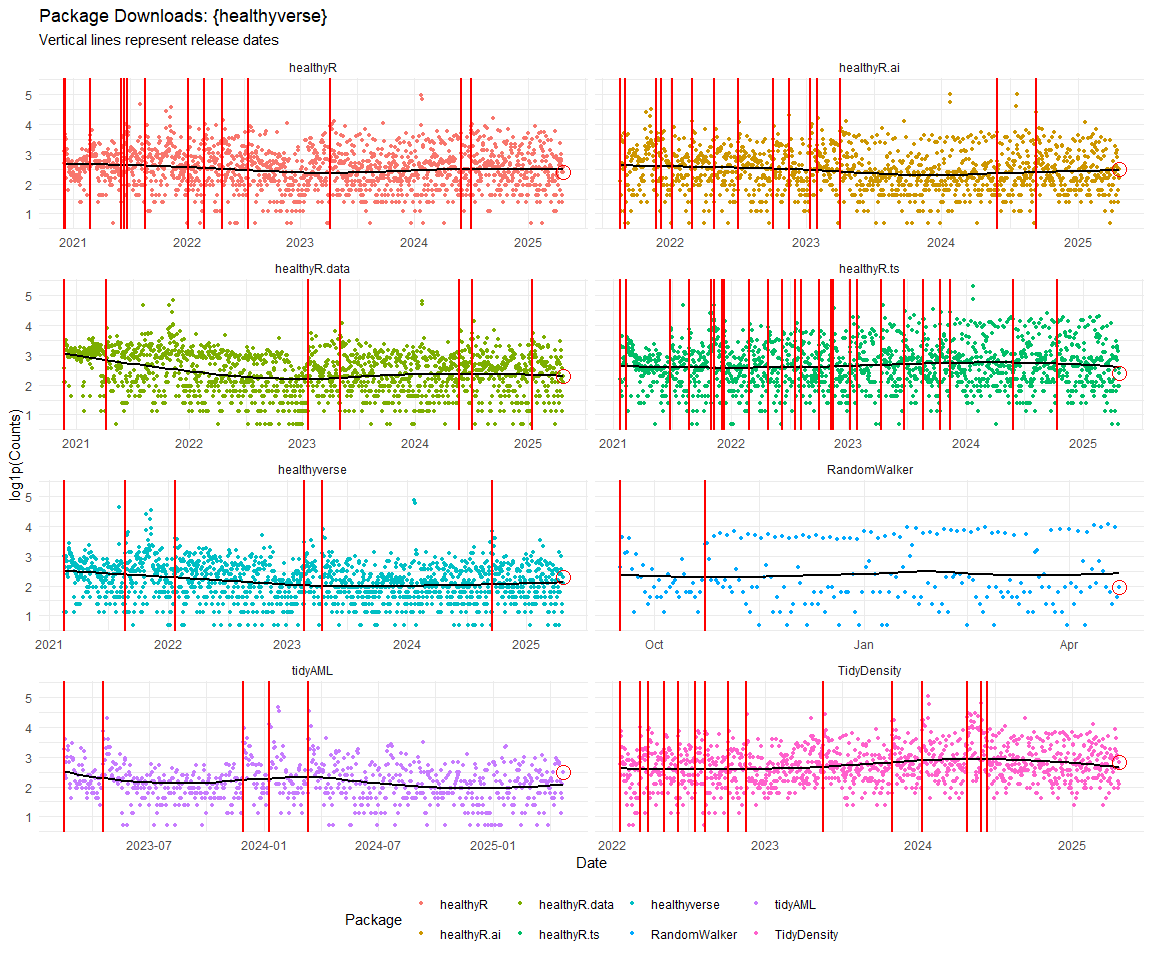
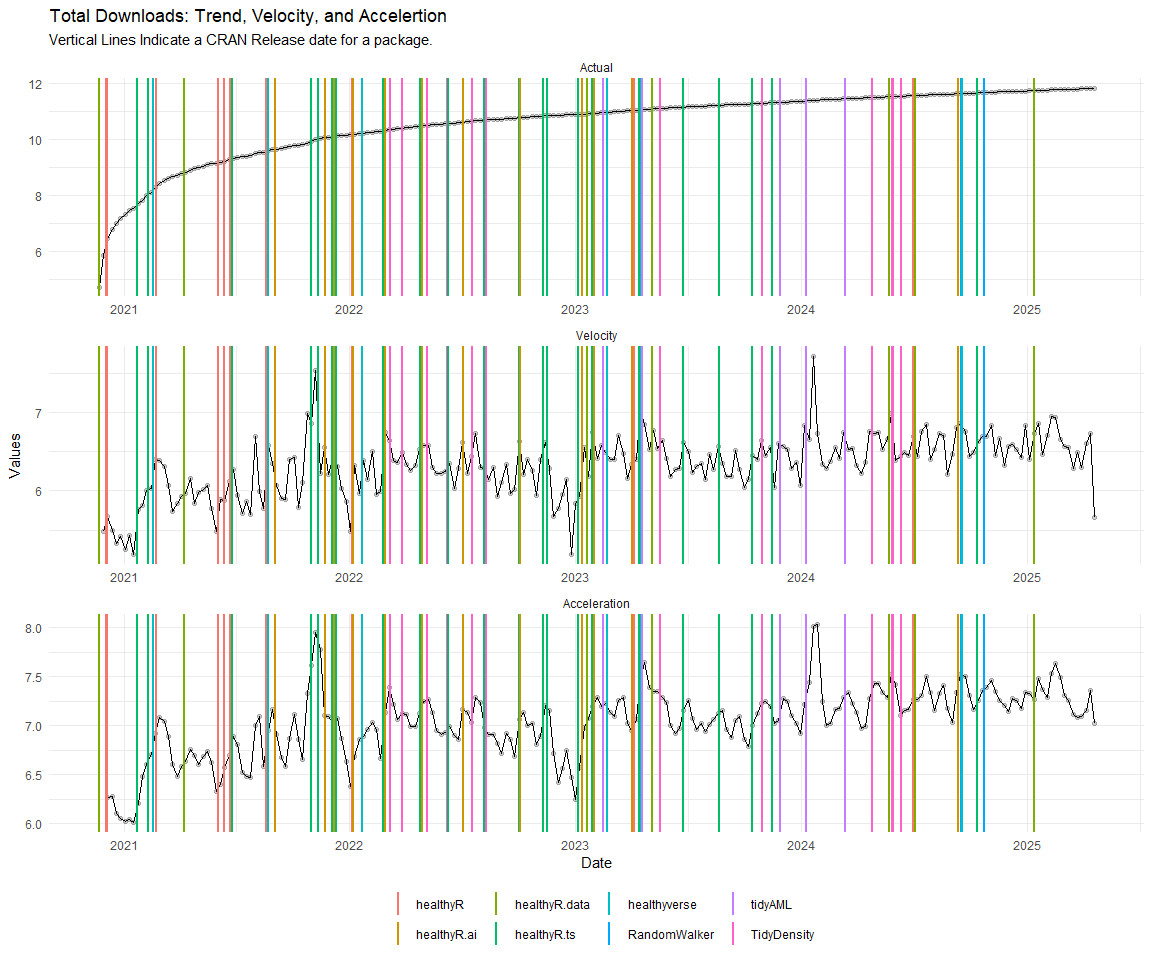
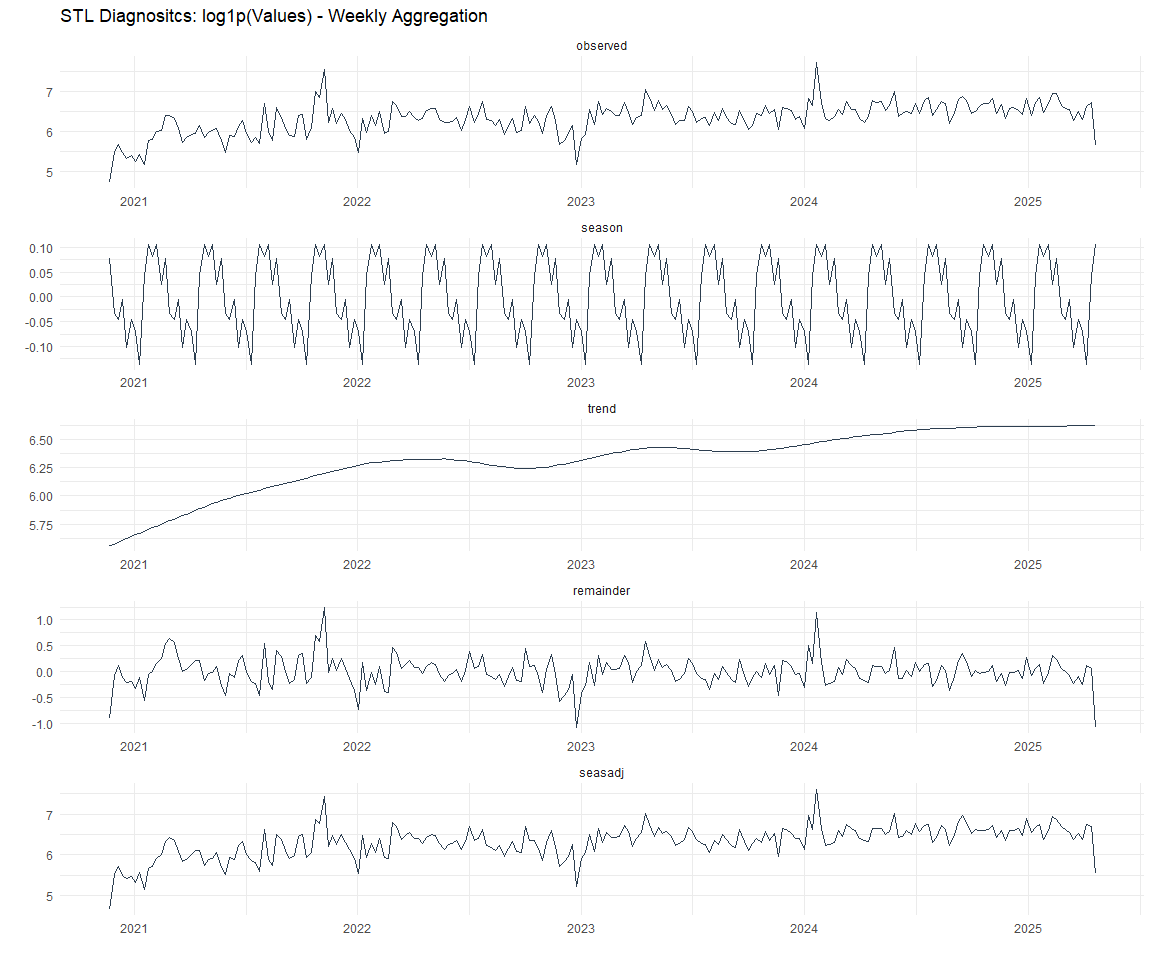
Now lets take a look at some time series decomposition graphs.
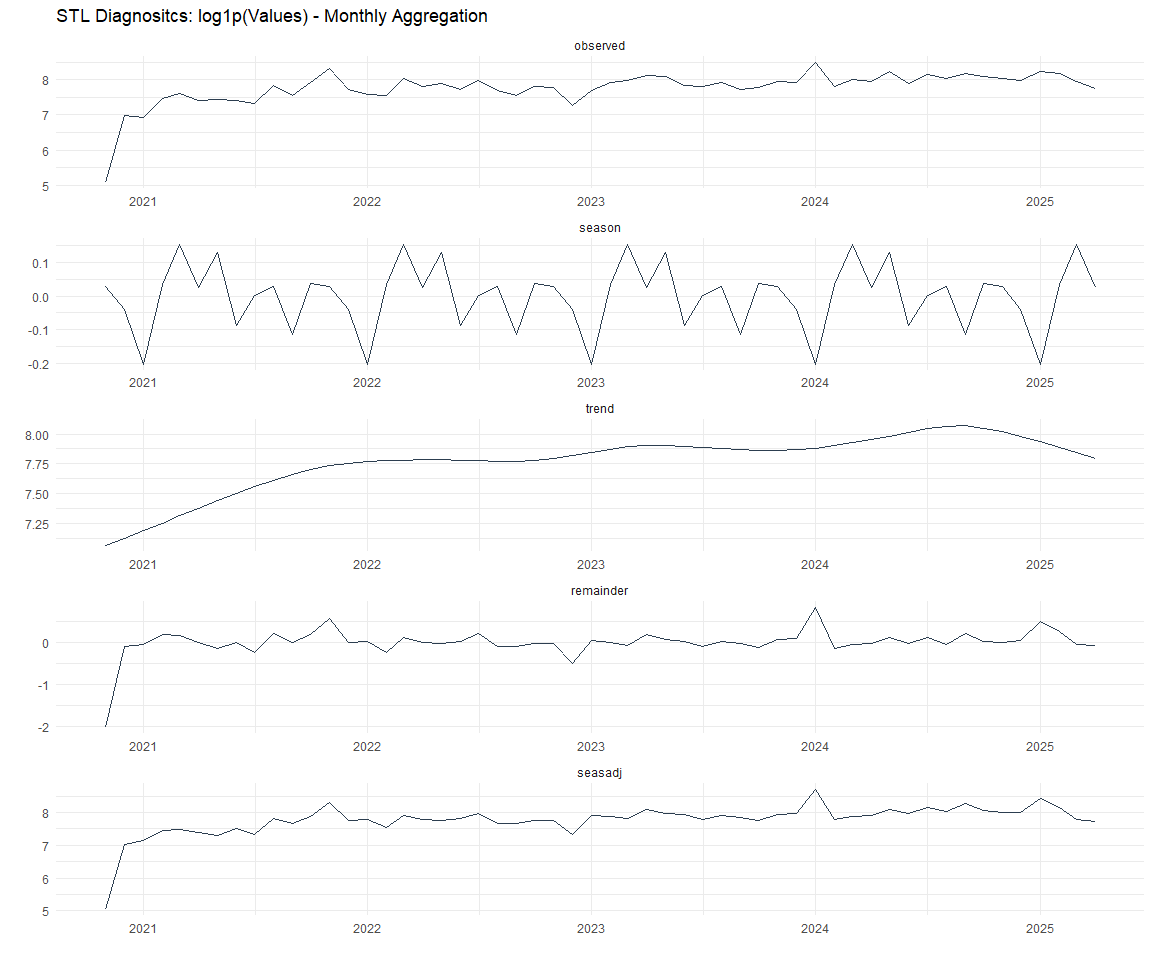
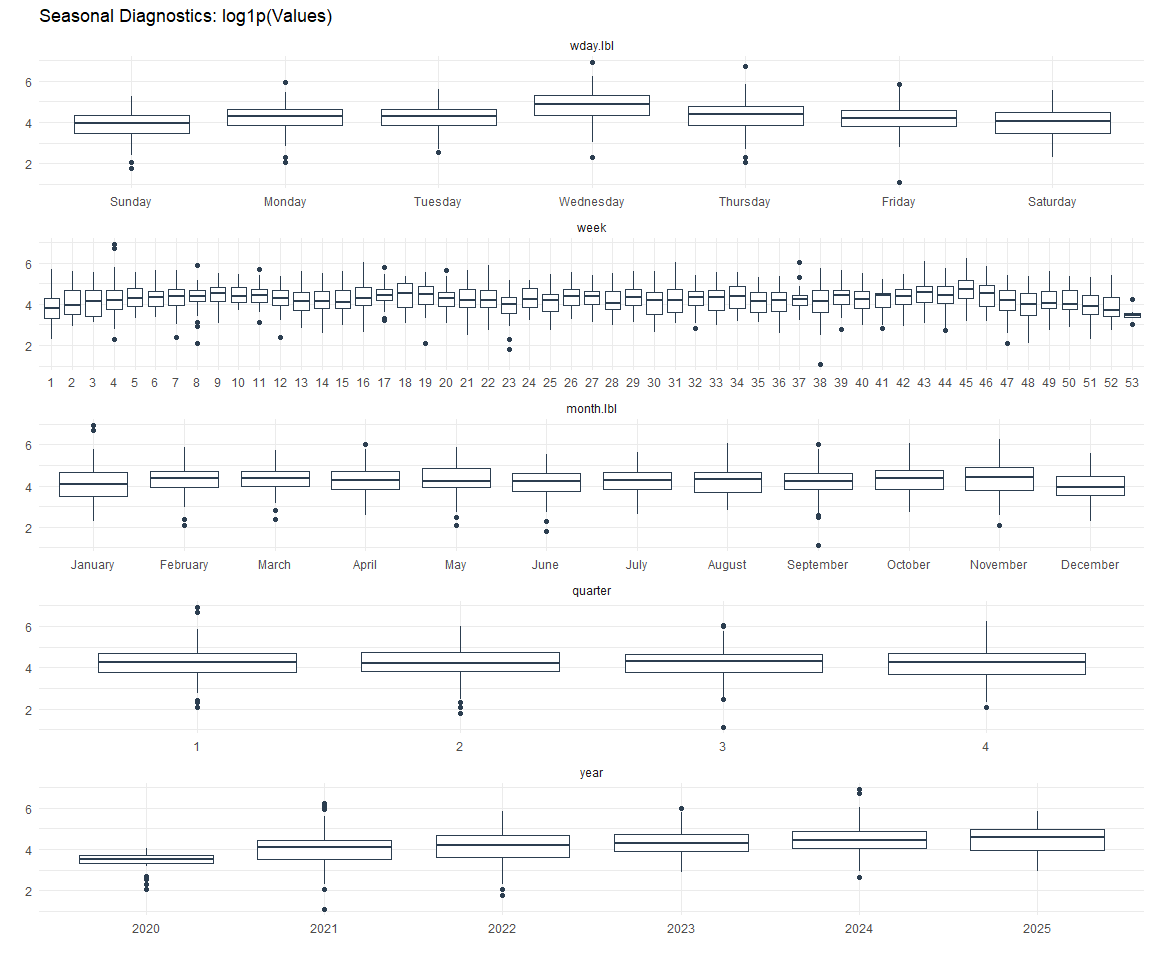
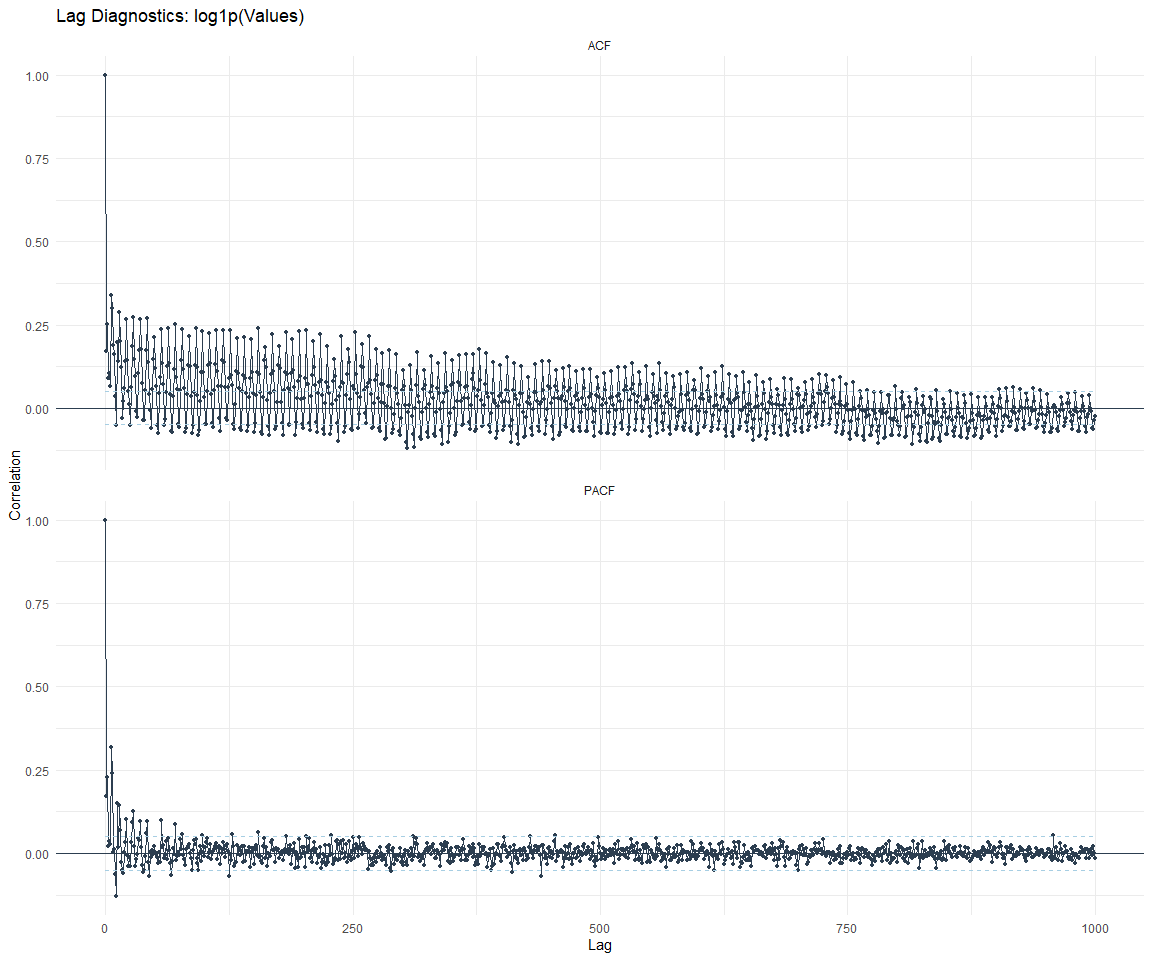
Feature Engineering
Now that we have our basic data and a shot of what it looks like, let’s
add some features to our data which can be very helpful in modeling.
Lets start by making a tibble that is aggregated by the day and
package, as we are going to be interested in forecasting the next 4
weeks or 28 days for each package. First lets get our base data.
##
## Call:
## stats::lm(formula = .formula, data = df)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -148.57 -36.06 -11.29 26.65 816.12
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error
## (Intercept) -1.715e+02 6.571e+01
## date 1.059e-02 3.479e-03
## lag(value, 1) 1.038e-01 2.410e-02
## lag(value, 7) 9.532e-02 2.493e-02
## lag(value, 14) 8.624e-02 2.493e-02
## lag(value, 21) 6.401e-02 2.497e-02
## lag(value, 28) 7.010e-02 2.497e-02
## lag(value, 35) 6.836e-02 2.505e-02
## lag(value, 42) 5.599e-02 2.517e-02
## lag(value, 49) 6.598e-02 2.505e-02
## month(date, label = TRUE).L -9.739e+00 5.108e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE).Q 3.426e+00 5.052e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE).C -1.326e+01 5.124e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^4 -6.899e+00 5.107e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^5 -1.134e+01 5.103e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^6 -4.040e+00 5.159e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^7 -7.057e+00 5.062e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^8 -3.075e+00 5.049e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^9 5.207e+00 5.039e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^10 2.686e+00 5.047e+00
## month(date, label = TRUE)^11 -3.598e+00 5.012e+00
## fourier_vec(date, type = "sin", K = 1, period = 7) -1.181e+01 2.304e+00
## fourier_vec(date, type = "cos", K = 1, period = 7) 8.097e+00 2.426e+00
## t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -2.610 0.009135 **
## date 3.045 0.002367 **
## lag(value, 1) 4.309 1.74e-05 ***
## lag(value, 7) 3.824 0.000136 ***
## lag(value, 14) 3.460 0.000555 ***
## lag(value, 21) 2.564 0.010451 *
## lag(value, 28) 2.807 0.005054 **
## lag(value, 35) 2.729 0.006416 **
## lag(value, 42) 2.224 0.026284 *
## lag(value, 49) 2.634 0.008523 **
## month(date, label = TRUE).L -1.907 0.056744 .
## month(date, label = TRUE).Q 0.678 0.497715
## month(date, label = TRUE).C -2.589 0.009713 **
## month(date, label = TRUE)^4 -1.351 0.176877
## month(date, label = TRUE)^5 -2.222 0.026417 *
## month(date, label = TRUE)^6 -0.783 0.433670
## month(date, label = TRUE)^7 -1.394 0.163494
## month(date, label = TRUE)^8 -0.609 0.542686
## month(date, label = TRUE)^9 1.033 0.301655
## month(date, label = TRUE)^10 0.532 0.594650
## month(date, label = TRUE)^11 -0.718 0.472898
## fourier_vec(date, type = "sin", K = 1, period = 7) -5.125 3.34e-07 ***
## fourier_vec(date, type = "cos", K = 1, period = 7) 3.337 0.000865 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 58.72 on 1618 degrees of freedom
## (49 observations deleted due to missingness)
## Multiple R-squared: 0.2377, Adjusted R-squared: 0.2273
## F-statistic: 22.93 on 22 and 1618 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
NNS Forecasting
This is something I have been wanting to try for a while. The NNS
package is a great package for forecasting time series data.
library(NNS)
data_list <- base_data |>
select(package, value) |>
group_split(package)
data_list |>
imap(
\(x, idx) {
obj <- x
x <- obj |> pull(value) |> tail(7*52)
train_set_size <- length(x) - 56
pkg <- obj |> pluck(1) |> unique()
sf <- NNS.seas(x, modulo = 7, plot = FALSE)$periods
cat(paste0("Package: ", pkg, "\n"))
NNS.ARMA.optim(
variable = x,
h = 28,
training.set = train_set_size,
#seasonal.factor = seq(12, 60, 7),
seasonal.factor = sf,
pred.int = 0.95,
plot = TRUE
)
title(
sub = paste0("\n",
"Package: ", pkg, " - NNS Optimization")
)
}
)
## Package: healthyR
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 21 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.17587359299776"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 21, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.1370918561817"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 21, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.1370918561817"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 21, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.69592915950719"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 21, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.69592915950719"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 21, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.05872411540146"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 21, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.05872411540146"
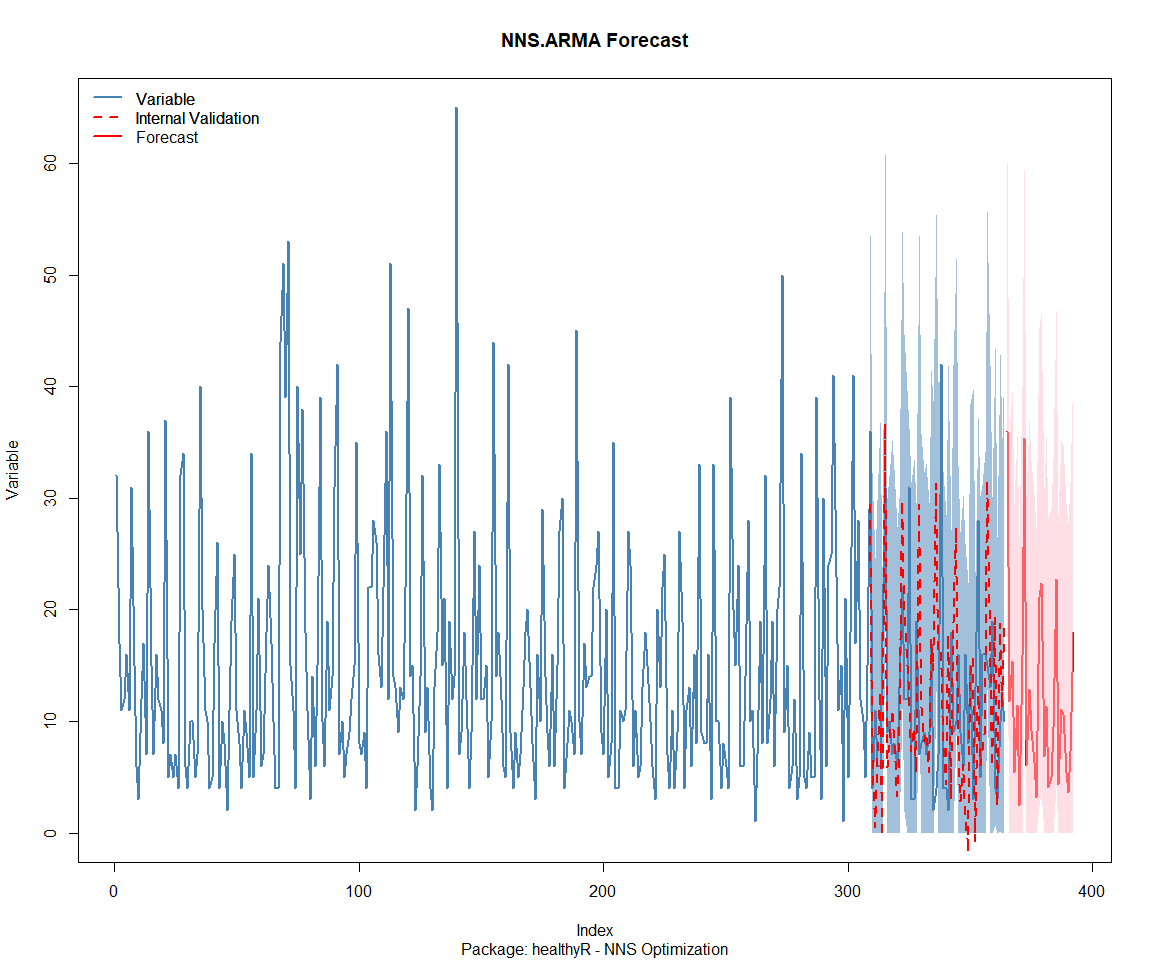
## Package: healthyR.ai
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.0528973402756"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.30657924351148"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.05752141579558"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.96368759619132"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.7666132615896"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.7666132615896"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 13.1182188548503"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 13.1182188548503"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 6.00697312606895"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 7, 42, 98, 63, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 6.00697312606895"
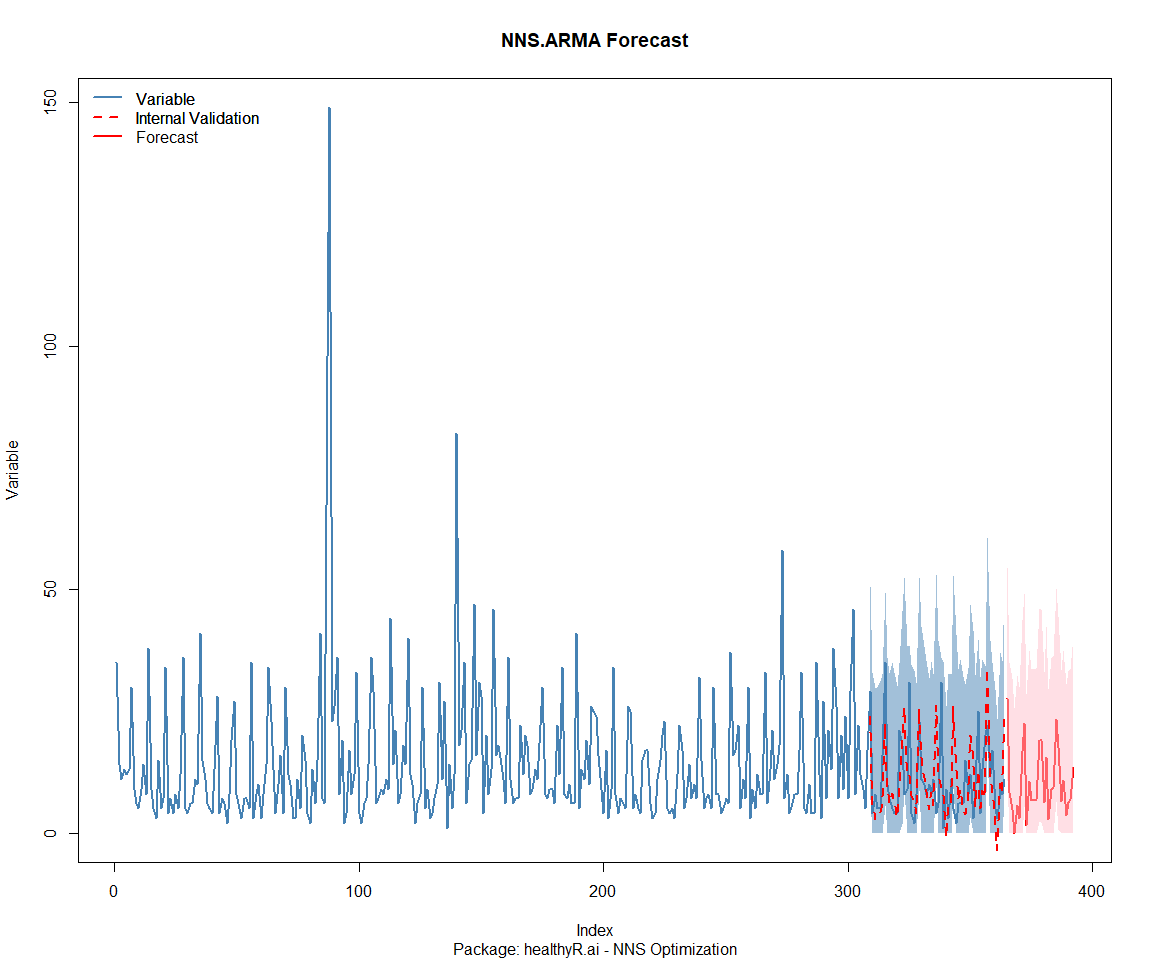
## Package: healthyR.data
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.05341213369132"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 42 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.44914809633861"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 77, 42 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.44914809633861"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 42 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.5578343613022"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 77, 42 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.5578343613022"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 42 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.33473715997021"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 77, 42 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.33473715997021"
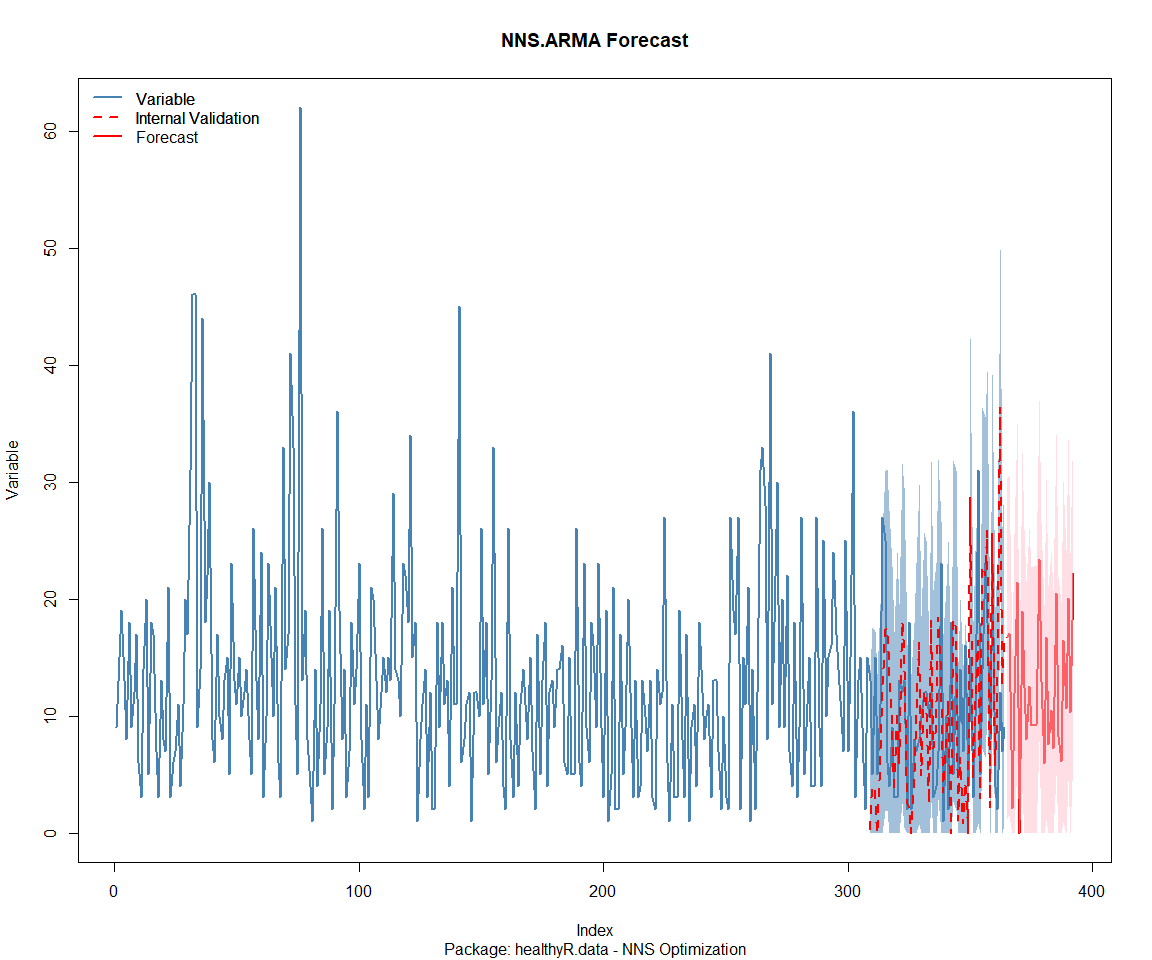
## Package: healthyR.ts
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.29497399360903"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 2.29497399360903"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 13.4768993948584"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 13.4768993948584"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.20769707481851"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.20769707481851"
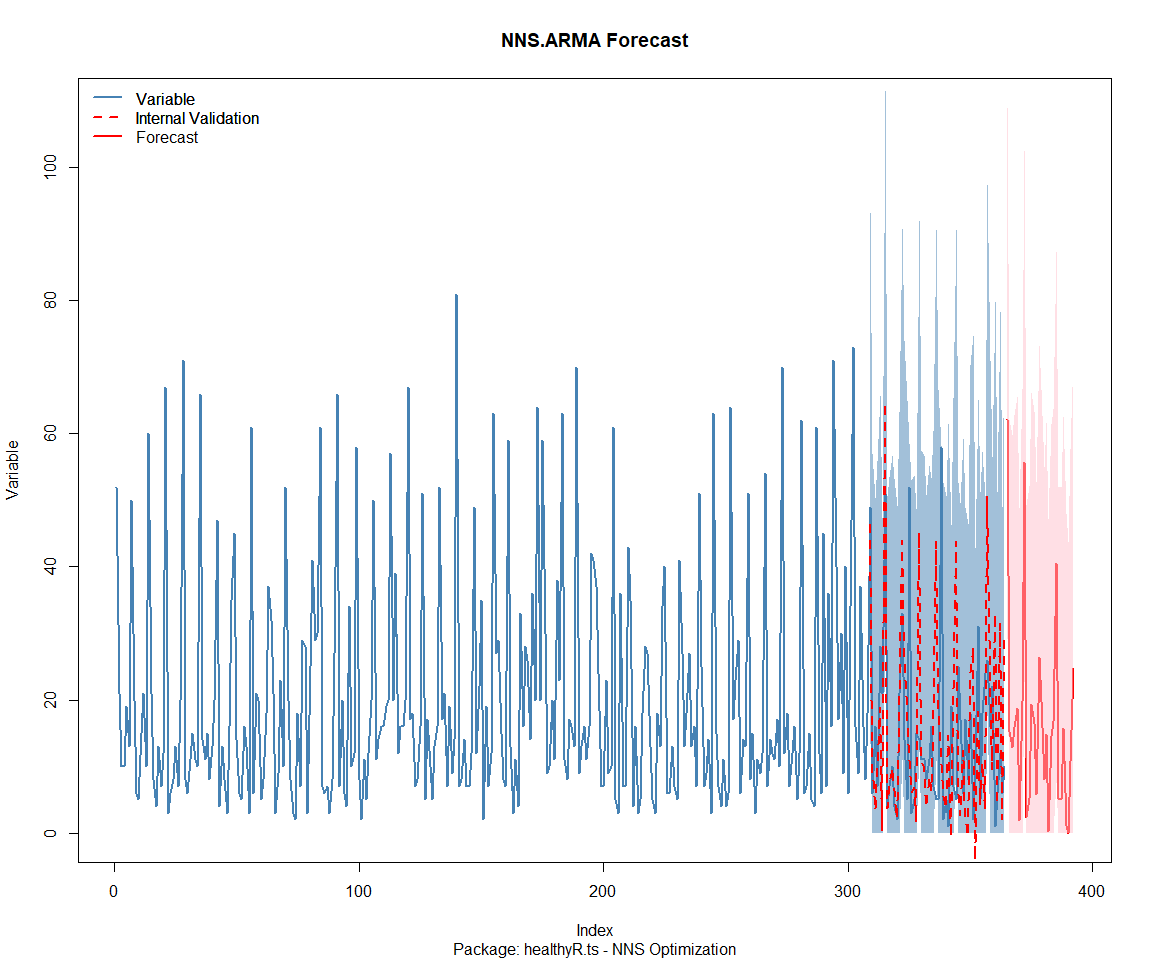
## Package: healthyverse
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.53926122858856"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63, 77 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.50742772414273"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 63, 77 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.50742772414273"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63, 77 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.66644932542882"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 63, 77 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.66644932542882"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 63, 77 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.07323823467052"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 63, 77 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.07323823467052"
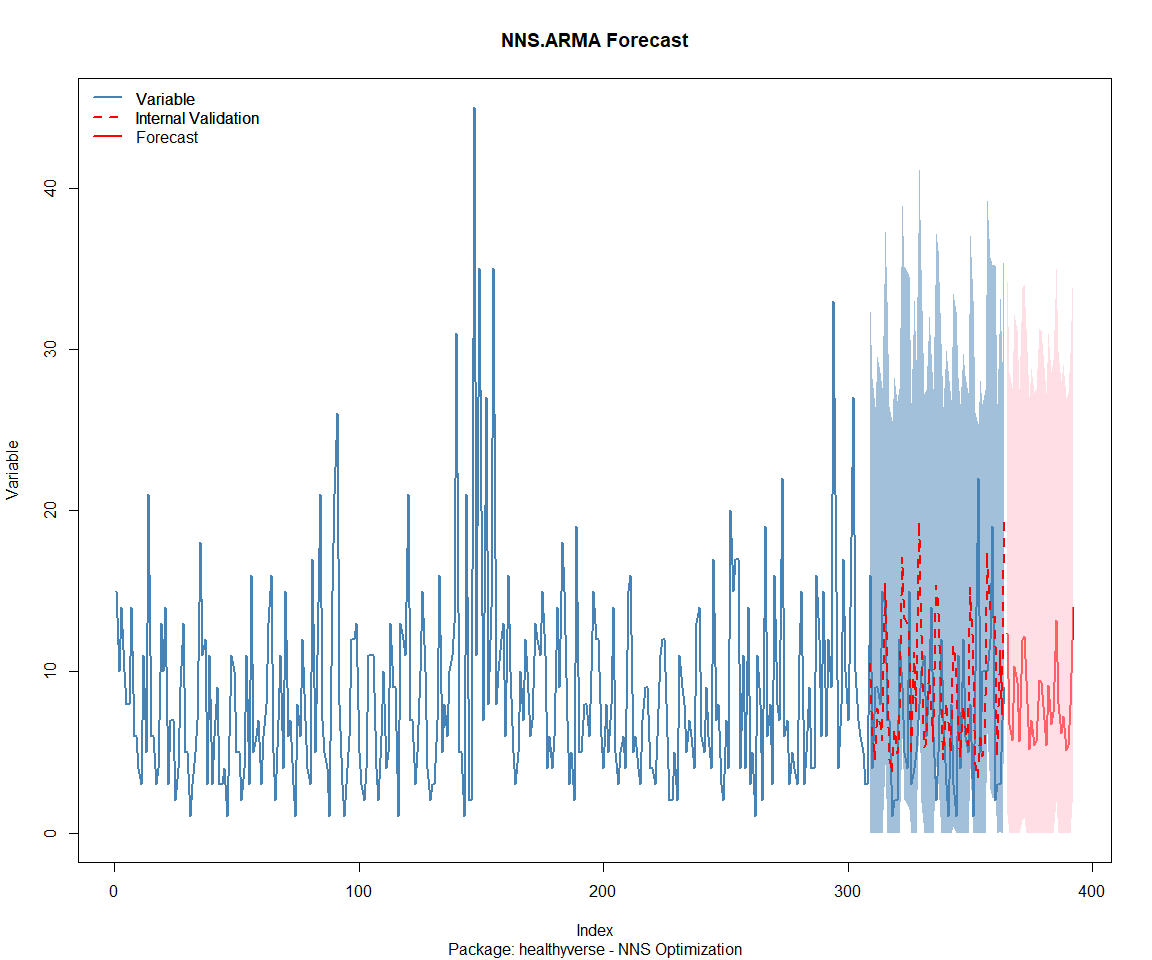
## Package: RandomWalker
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.85154383501843"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.36207745735206"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 77, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.36207745735206"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.63264601972759"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 77, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.63264601972759"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 77, 49 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.33340955875847"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 77, 49 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 1.33340955875847"
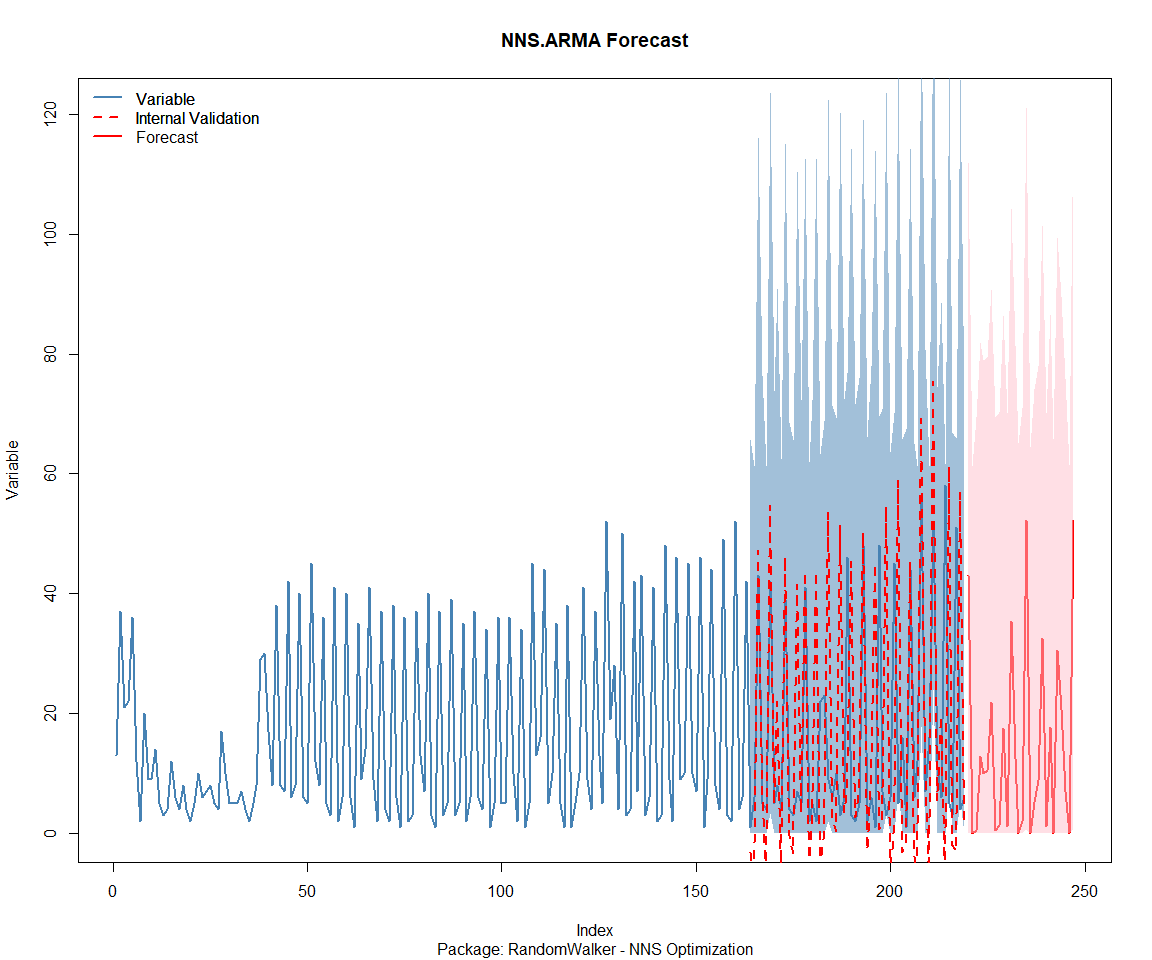
## Package: tidyAML
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 84 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 4.33067812514487"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 84, 35 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.97281705819193"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 84, 35, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.90032092773926"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 84, 35, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.90032092773926"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 84, 35, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.70069972737091"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 84, 35, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.70069972737091"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 84, 35, 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.25720775855832"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 84, 35, 63 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.25720775855832"
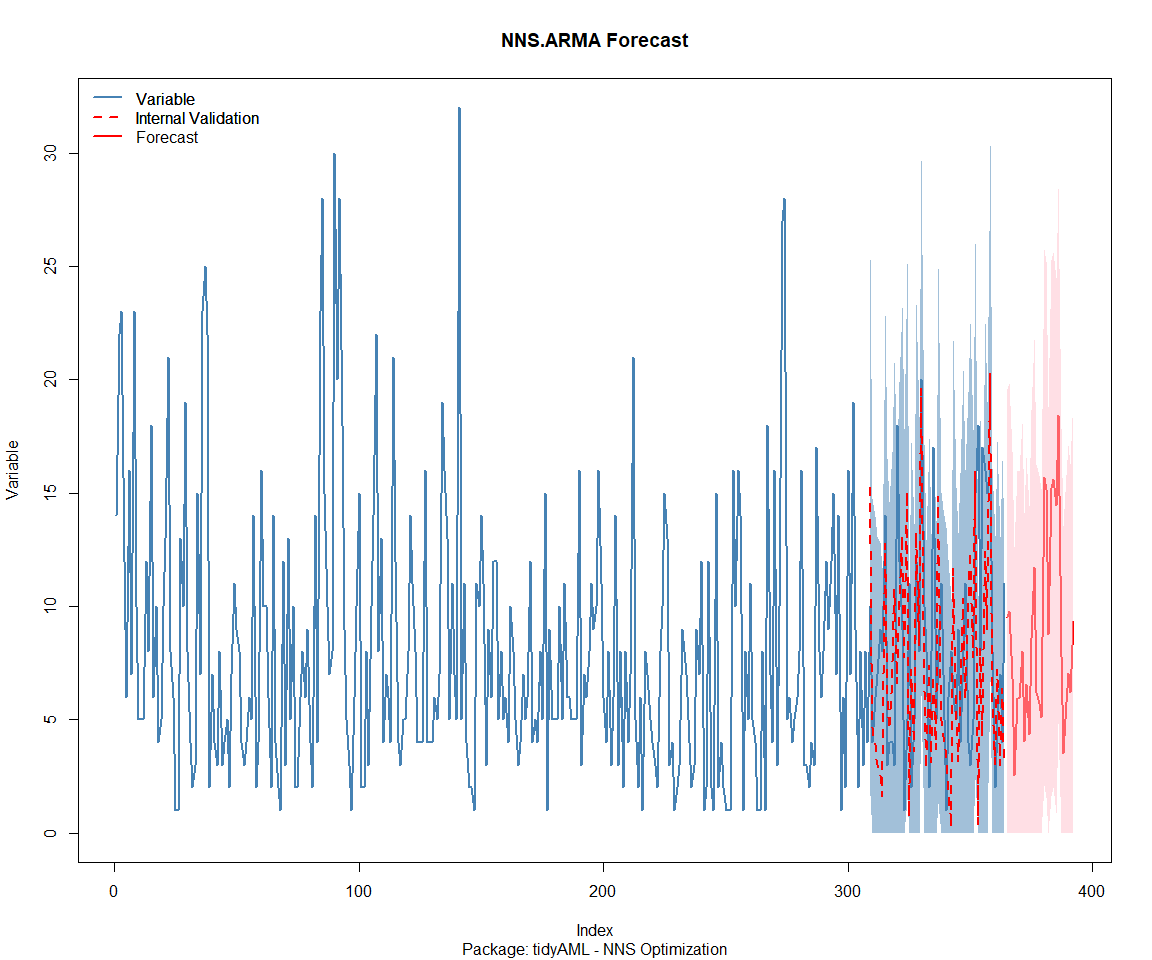
## Package: TidyDensity
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: lin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'lin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.11991535431211"
## [1] "BEST method = 'lin', seasonal.factor = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST lin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 3.11991535431211"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: nonlin"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'nonlin' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 9.95838642568237"
## [1] "BEST method = 'nonlin' PATH MEMBER = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST nonlin OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 9.95838642568237"
## [1] "CURRNET METHOD: both"
## [1] "COPY LATEST PARAMETERS DIRECTLY FOR NNS.ARMA() IF ERROR:"
## [1] "NNS.ARMA(... method = 'both' , seasonal.factor = c( 63 ) ...)"
## [1] "CURRENT both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.78273503609249"
## [1] "BEST method = 'both' PATH MEMBER = c( 63 )"
## [1] "BEST both OBJECTIVE FUNCTION = 5.78273503609249"
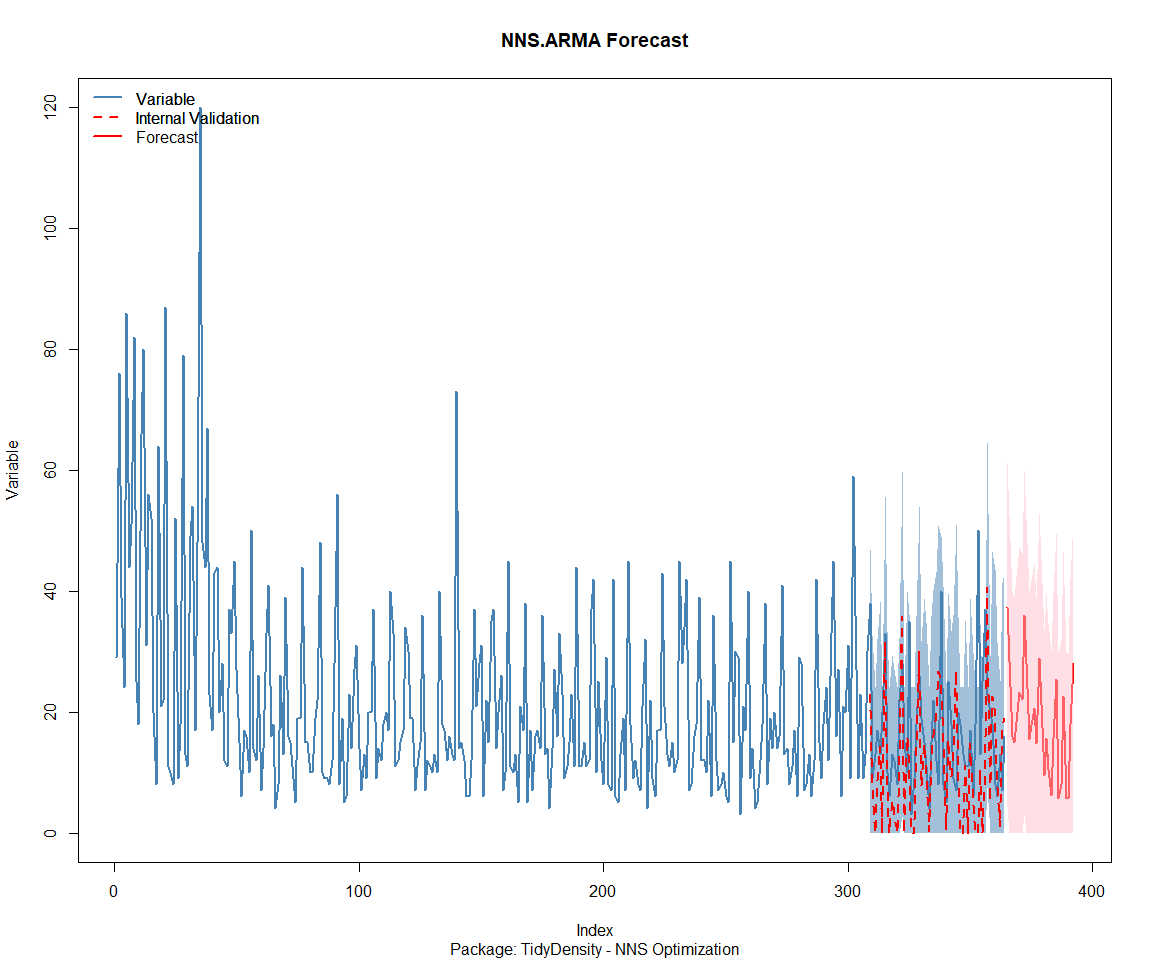
## [[1]]
## NULL
##
## [[2]]
## NULL
##
## [[3]]
## NULL
##
## [[4]]
## NULL
##
## [[5]]
## NULL
##
## [[6]]
## NULL
##
## [[7]]
## NULL
##
## [[8]]
## NULL
Pre-Processing
Now we are going to do some basic pre-processing.
data_padded_tbl <- base_data %>%
pad_by_time(
.date_var = date,
.pad_value = 0
)
# Get log interval and standardization parameters
log_params <- liv(data_padded_tbl$value, limit_lower = 0, offset = 1, silent = TRUE)
limit_lower <- log_params$limit_lower
limit_upper <- log_params$limit_upper
offset <- log_params$offset
data_liv_tbl <- data_padded_tbl %>%
# Get log interval transform
mutate(value_trans = liv(value, limit_lower = 0, offset = 1, silent = TRUE)$log_scaled)
# Get Standardization Params
std_params <- standard_vec(data_liv_tbl$value_trans, silent = TRUE)
std_mean <- std_params$mean
std_sd <- std_params$sd
data_transformed_tbl <- data_liv_tbl %>%
# get standardization
mutate(value_trans = standard_vec(value_trans, silent = TRUE)$standard_scaled) %>%
select(-value)
Since this is panel data we can follow one of two different modeling strategies. We can search for a global model in the panel data or we can use nested forecasting finding the best model for each of the time series. Since we only have 5 panels, we will use nested forecasting.
To do this we will use the nest_timeseries and
split_nested_timeseries functions to create a nested tibble.
horizon <- 4*7
nested_data_tbl <- data_transformed_tbl %>%
# 1. Extending: We'll predict n days into the future.
extend_timeseries(
.id_var = package,
.date_var = date,
.length_future = horizon
) %>%
# 2. Nesting: We'll group by id, and create a future dataset
# that forecasts n days of extended data and
# an actual dataset that contains n*2 days
nest_timeseries(
.id_var = package,
.length_future = horizon
#.length_actual = horizon*2
) %>%
# 3. Splitting: We'll take the actual data and create splits
# for accuracy and confidence interval estimation of n das (test)
# and the rest is training data
split_nested_timeseries(
.length_test = horizon
)
nested_data_tbl
## # A tibble: 8 × 4
## package .actual_data .future_data .splits
## <fct> <list> <list> <list>
## 1 healthyR.data <tibble [1,682 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1654|28]>
## 2 healthyR <tibble [1,676 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1648|28]>
## 3 healthyR.ts <tibble [1,620 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1592|28]>
## 4 healthyverse <tibble [1,590 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1562|28]>
## 5 healthyR.ai <tibble [1,415 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1387|28]>
## 6 TidyDensity <tibble [1,266 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [1238|28]>
## 7 tidyAML <tibble [874 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [846|28]>
## 8 RandomWalker <tibble [296 × 2]> <tibble [28 × 2]> <split [268|28]>
Now it is time to make some recipes and models using the modeltime workflow.
Modeltime Workflow
Recipe Object
recipe_base <- recipe(
value_trans ~ date
, data = extract_nested_test_split(nested_data_tbl)
)
recipe_base
recipe_date <- recipe_base %>%
step_mutate(date = as.numeric(date))
Models
# Models ------------------------------------------------------------------
# Auto ARIMA --------------------------------------------------------------
model_spec_arima_no_boost <- arima_reg() %>%
set_engine(engine = "auto_arima")
wflw_auto_arima <- workflow() %>%
add_recipe(recipe = recipe_base) %>%
add_model(model_spec_arima_no_boost)
# NNETAR ------------------------------------------------------------------
model_spec_nnetar <- nnetar_reg(
mode = "regression"
, seasonal_period = "auto"
) %>%
set_engine("nnetar")
wflw_nnetar <- workflow() %>%
add_recipe(recipe = recipe_base) %>%
add_model(model_spec_nnetar)
# TSLM --------------------------------------------------------------------
model_spec_lm <- linear_reg() %>%
set_engine("lm")
wflw_lm <- workflow() %>%
add_recipe(recipe = recipe_base) %>%
add_model(model_spec_lm)
# MARS --------------------------------------------------------------------
model_spec_mars <- mars(mode = "regression") %>%
set_engine("earth")
wflw_mars <- workflow() %>%
add_recipe(recipe = recipe_base) %>%
add_model(model_spec_mars)
Nested Modeltime Tables
nested_modeltime_tbl <- modeltime_nested_fit(
# Nested Data
nested_data = nested_data_tbl,
control = control_nested_fit(
verbose = TRUE,
allow_par = FALSE
),
# Add workflows
wflw_auto_arima,
wflw_lm,
wflw_mars,
wflw_nnetar
)
nested_modeltime_tbl <- nested_modeltime_tbl[!is.na(nested_modeltime_tbl$package),]
Model Accuracy
nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
extract_nested_test_accuracy() %>%
filter(!is.na(package)) %>%
knitr::kable()
| package | .model_id | .model_desc | .type | mae | mape | mase | smape | rmse | rsq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| healthyR.data | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.6559795 | 135.75522 | 0.8378498 | 129.92292 | 0.7861493 | 0.0022702 |
| healthyR.data | 2 | LM | Test | 0.6523690 | 132.92048 | 0.8332383 | 123.44746 | 0.7907810 | 0.0186310 |
| healthyR.data | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| healthyR.data | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.6887490 | 104.74725 | 0.8797045 | 196.75470 | 0.8151269 | 0.0603905 |
| healthyR | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.7051811 | 173.86954 | 0.7369230 | 143.25694 | 0.9513492 | 0.0058341 |
| healthyR | 2 | LM | Test | 0.6526995 | 101.38382 | 0.6820792 | 147.53166 | 0.9194564 | 0.0030432 |
| healthyR | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| healthyR | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.6638089 | 112.03951 | 0.6936887 | 147.60290 | 0.9271330 | 0.0115741 |
| healthyR.ts | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.7098817 | 171.32590 | 0.7202452 | 143.52597 | 0.8784269 | 0.0447699 |
| healthyR.ts | 2 | LM | Test | 0.7125015 | 156.06193 | 0.7229033 | 130.82876 | 0.9154122 | 0.0503220 |
| healthyR.ts | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| healthyR.ts | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.6138347 | 98.54818 | 0.6227961 | 153.39440 | 0.7727641 | 0.2519968 |
| healthyverse | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.6858541 | 284.60786 | 0.7845918 | 94.66784 | 0.8727095 | 0.2736955 |
| healthyverse | 2 | LM | Test | 0.6408968 | 263.81065 | 0.7331624 | 92.41764 | 0.8269133 | 0.0001477 |
| healthyverse | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| healthyverse | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.5860949 | 152.93919 | 0.6704710 | 96.64632 | 0.8153433 | 0.0057779 |
| healthyR.ai | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.5936534 | 110.62322 | 0.8049599 | 146.87037 | 0.7350576 | 0.0014387 |
| healthyR.ai | 2 | LM | Test | 0.5842708 | 106.75330 | 0.7922376 | 144.74853 | 0.7337600 | 0.0000812 |
| healthyR.ai | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| healthyR.ai | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.5819298 | 99.98772 | 0.7890633 | 154.64590 | 0.7175413 | 0.0562157 |
| TidyDensity | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.5428721 | 88.19204 | 0.7286846 | 111.64815 | 0.7525904 | 0.0179498 |
| TidyDensity | 2 | LM | Test | 0.4988245 | 117.61797 | 0.6695606 | 81.31340 | 0.7074143 | 0.0042458 |
| TidyDensity | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| TidyDensity | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.5879371 | 90.51231 | 0.7891743 | 126.49423 | 0.7942406 | 0.0082549 |
| tidyAML | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 0.5785670 | 210.18827 | 0.8491117 | 93.62382 | 0.7177850 | 0.0045363 |
| tidyAML | 2 | LM | Test | 0.5678711 | 199.34620 | 0.8334144 | 95.36030 | 0.6960433 | 0.0301224 |
| tidyAML | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| tidyAML | 4 | NNAR | Test | 0.5702857 | 204.37390 | 0.8369580 | 94.04757 | 0.7048633 | 0.0003562 |
| RandomWalker | 1 | ARIMA | Test | 1.1462802 | 125.51044 | 0.6479563 | 162.73456 | 1.3498524 | 0.0111619 |
| RandomWalker | 2 | LM | Test | 1.0690180 | 97.76723 | 0.6042824 | 187.83285 | 1.2358225 | 0.0075489 |
| RandomWalker | 3 | NULL | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| RandomWalker | 4 | NNAR | Test | 1.0547882 | 141.65719 | 0.5962388 | 148.82795 | 1.1783665 | 0.0934410 |
Plot Models
nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
extract_nested_test_forecast() %>%
group_by(package) %>%
plot_modeltime_forecast(
.interactive = FALSE,
.conf_interval_show = FALSE,
.facet_scales = "free"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
Best Model
best_nested_modeltime_tbl <- nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
modeltime_nested_select_best(
metric = "rmse",
minimize = TRUE,
filter_test_forecasts = TRUE
)
best_nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
extract_nested_best_model_report()
## # Nested Modeltime Table
##
## # A tibble: 8 × 10
## package .model_id .model_desc .type mae mape mase smape rmse rsq
## <fct> <int> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 healthyR.da… 1 ARIMA Test 0.656 136. 0.838 130. 0.786 0.00227
## 2 healthyR 2 LM Test 0.653 101. 0.682 148. 0.919 0.00304
## 3 healthyR.ts 4 NNAR Test 0.614 98.5 0.623 153. 0.773 0.252
## 4 healthyverse 4 NNAR Test 0.586 153. 0.670 96.6 0.815 0.00578
## 5 healthyR.ai 4 NNAR Test 0.582 100.0 0.789 155. 0.718 0.0562
## 6 TidyDensity 2 LM Test 0.499 118. 0.670 81.3 0.707 0.00425
## 7 tidyAML 2 LM Test 0.568 199. 0.833 95.4 0.696 0.0301
## 8 RandomWalker 4 NNAR Test 1.05 142. 0.596 149. 1.18 0.0934
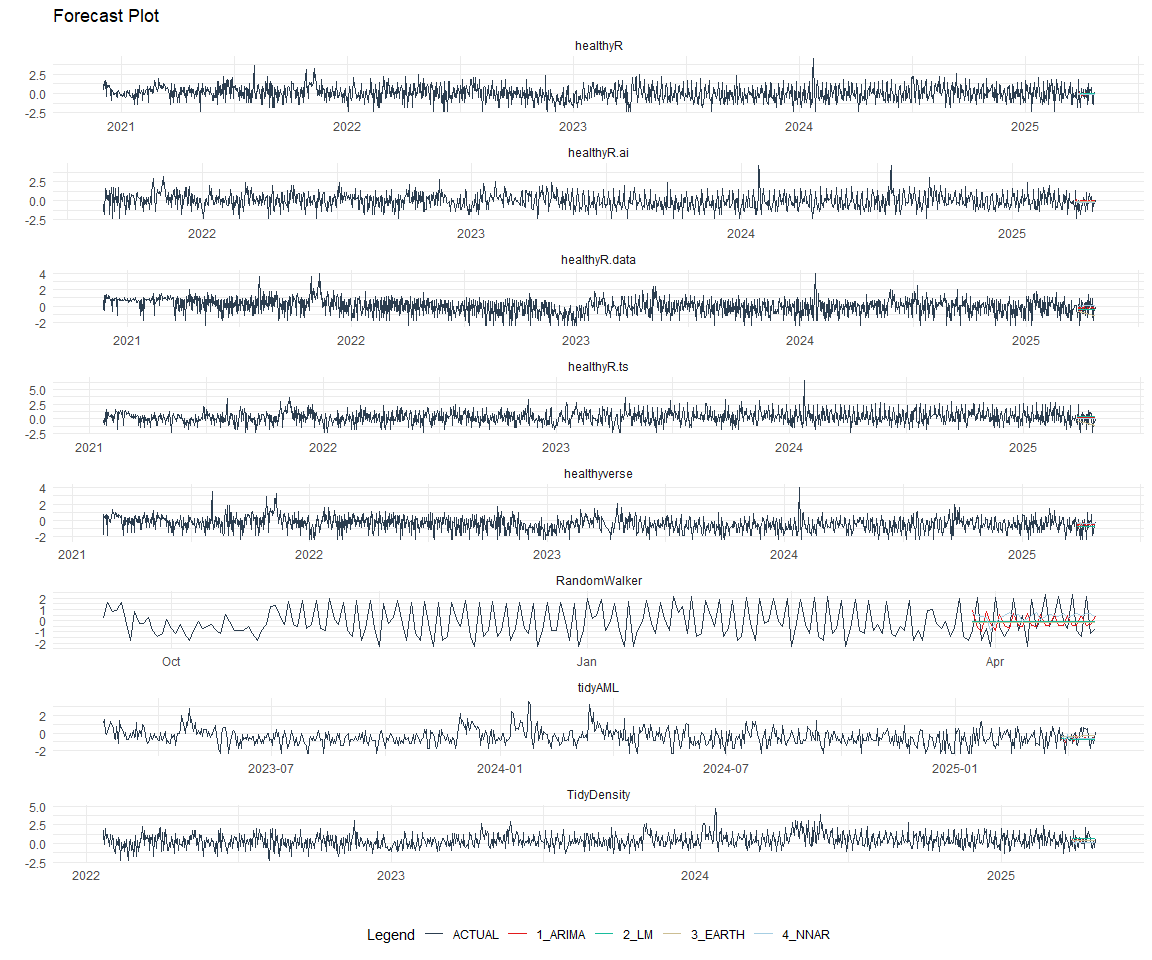
best_nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
extract_nested_test_forecast() %>%
#filter(!is.na(.model_id)) %>%
group_by(package) %>%
plot_modeltime_forecast(
.interactive = FALSE,
.conf_interval_alpha = 0.2,
.facet_scales = "free"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
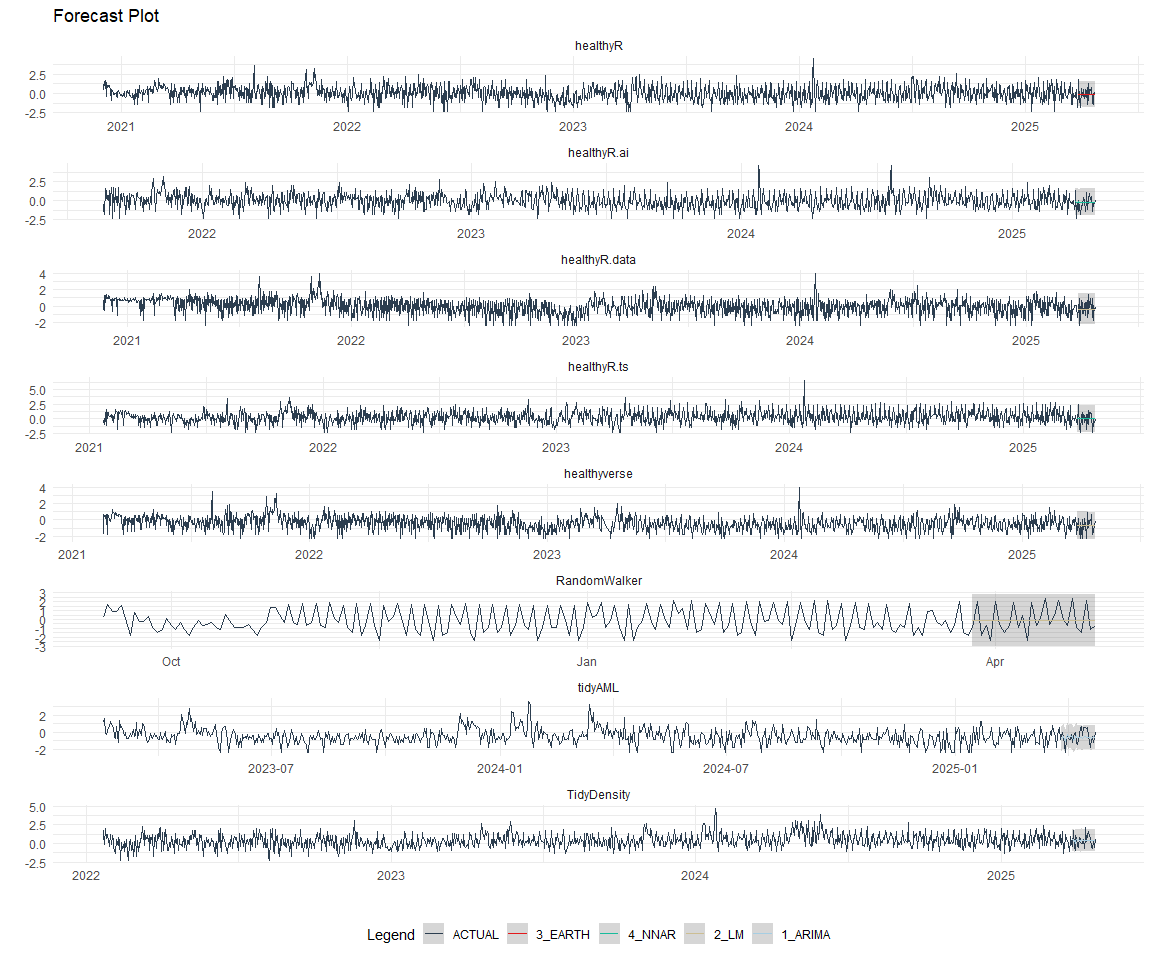
Refitting and Future Forecast
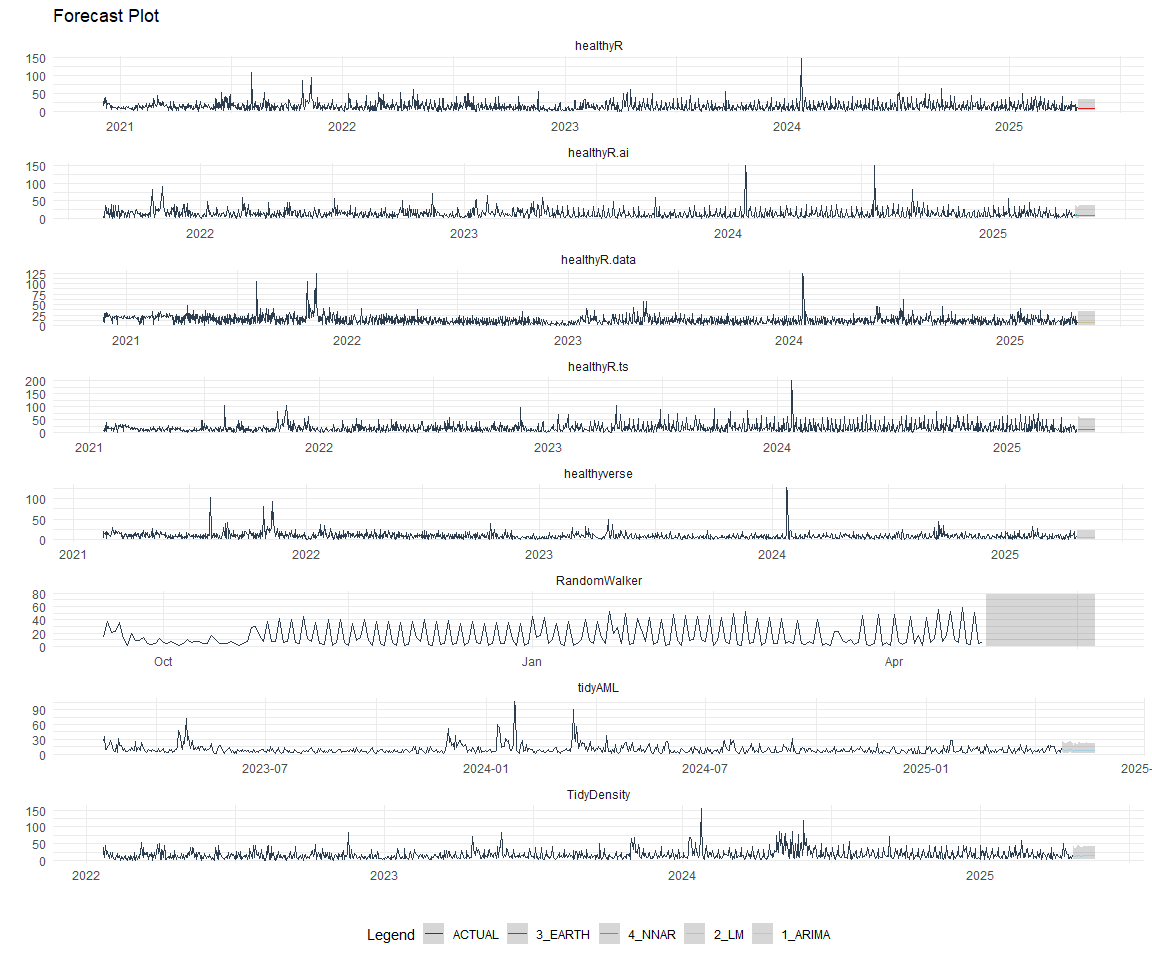
Now that we have the best models, we can make our future forecasts.
nested_modeltime_refit_tbl <- best_nested_modeltime_tbl %>%
modeltime_nested_refit(
control = control_nested_refit(verbose = TRUE)
)
nested_modeltime_refit_tbl
## # Nested Modeltime Table
##
## # A tibble: 8 × 5
## package .actual_data .future_data .splits .modeltime_tables
## <fct> <list> <list> <list> <list>
## 1 healthyR.data <tibble> <tibble> <split [1654|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 2 healthyR <tibble> <tibble> <split [1648|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 3 healthyR.ts <tibble> <tibble> <split [1592|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 4 healthyverse <tibble> <tibble> <split [1562|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 5 healthyR.ai <tibble> <tibble> <split [1387|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 6 TidyDensity <tibble> <tibble> <split [1238|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 7 tidyAML <tibble> <tibble> <split [846|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
## 8 RandomWalker <tibble> <tibble> <split [268|28]> <mdl_tm_t [1 × 5]>
nested_modeltime_refit_tbl %>%
extract_nested_future_forecast() %>%
mutate(across(.value:.conf_hi, .fns = ~ standard_inv_vec(
x = .,
mean = std_mean,
sd = std_sd
)$standard_inverse_value)) %>%
mutate(across(.value:.conf_hi, .fns = ~ liiv(
x = .,
limit_lower = limit_lower,
limit_upper = limit_upper,
offset = offset
)$rescaled_v)) %>%
group_by(package) %>%
plot_modeltime_forecast(
.interactive = FALSE,
.conf_interval_alpha = 0.2,
.facet_scales = "free"
) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")