Bootstrap resampling is a powerful statistical technique for robust inference. TidyDensity provides integrated bootstrap functionality with seamless visualization and analysis tools.
What is Bootstrap?
Concept
Bootstrap resampling is a non-parametric method for:
- Estimating sampling distributions
- Calculating confidence intervals
- Assessing parameter uncertainty
- Making inferences without distributional assumptions
Bootstrap in TidyDensity
Main Function: tidy_bootstrap()
Generate bootstrap samples in tidy format:
tidy_bootstrap(
.x, # Your data vector
.num_sims = 2000, # Number of bootstrap samples
.proportion = 0.8, # Proportion to sample (default = 0.8)
.distribution_type = "continuous" # continuous or discrete
)Basic Bootstrap Analysis
Simple Bootstrap Example
# Your data
data <- mtcars$mpg
# Perform bootstrap
bootstrap_data <- tidy_bootstrap(
.x = data,
.num_sims = 2000
)
# View structure
head(bootstrap_data)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 2
#> sim_number bootstrap_samples
#> <fct> <list>
#> 1 1 <dbl [25]>
#> 2 2 <dbl [25]>
#> 3 3 <dbl [25]>
#> 4 4 <dbl [25]>
#> 5 5 <dbl [25]>
#> 6 6 <dbl [25]>Visualizing Bootstrap Distribution
# Density plot of bootstrap distribution Cumulative Mean
bootstrap_stat_plot(bootstrap_data, .value = y, .stat = "cmean")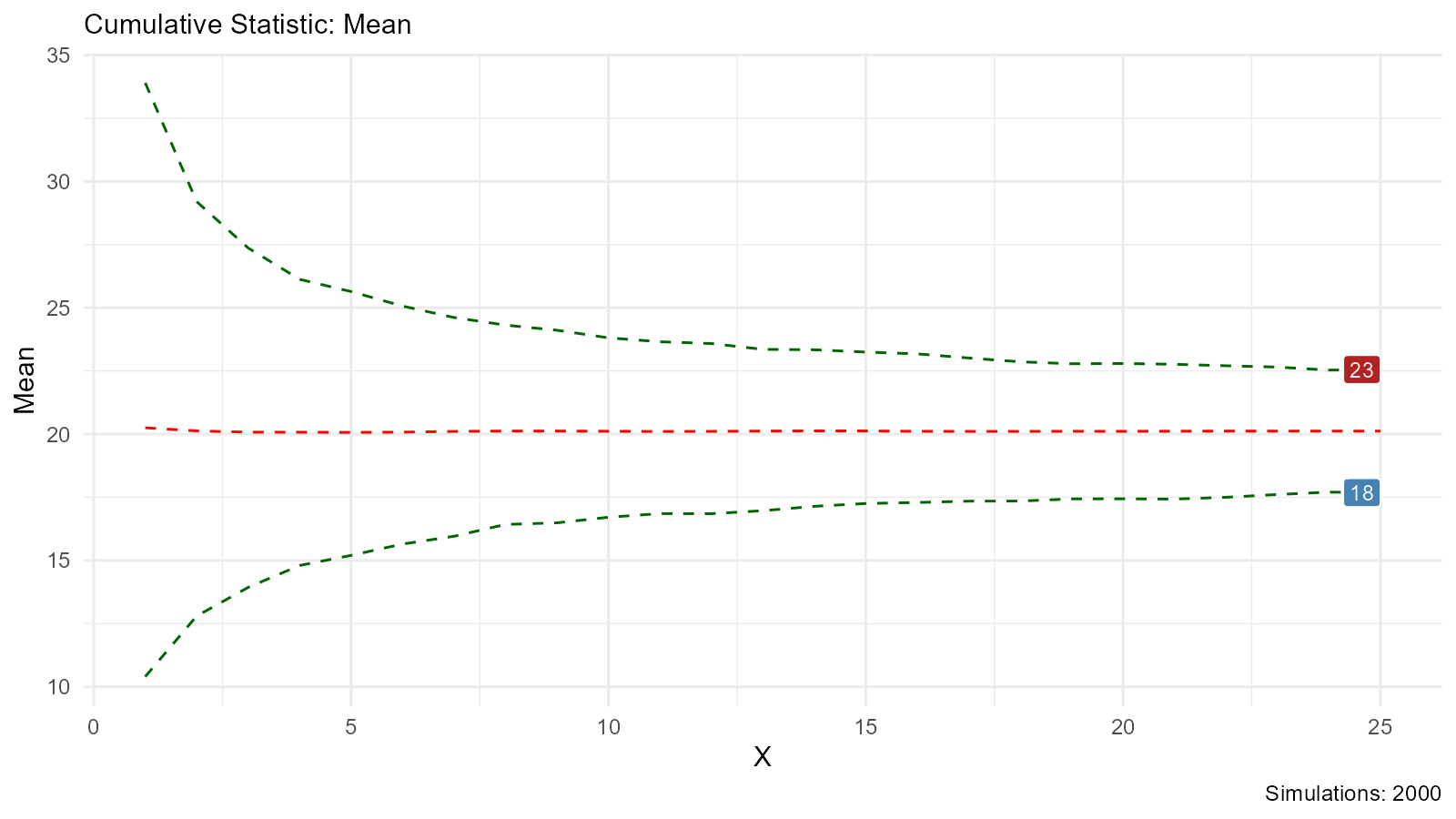
# Cumulative Harmonic Mean
bootstrap_stat_plot(bootstrap_data, .value = y, .stat = "chmean")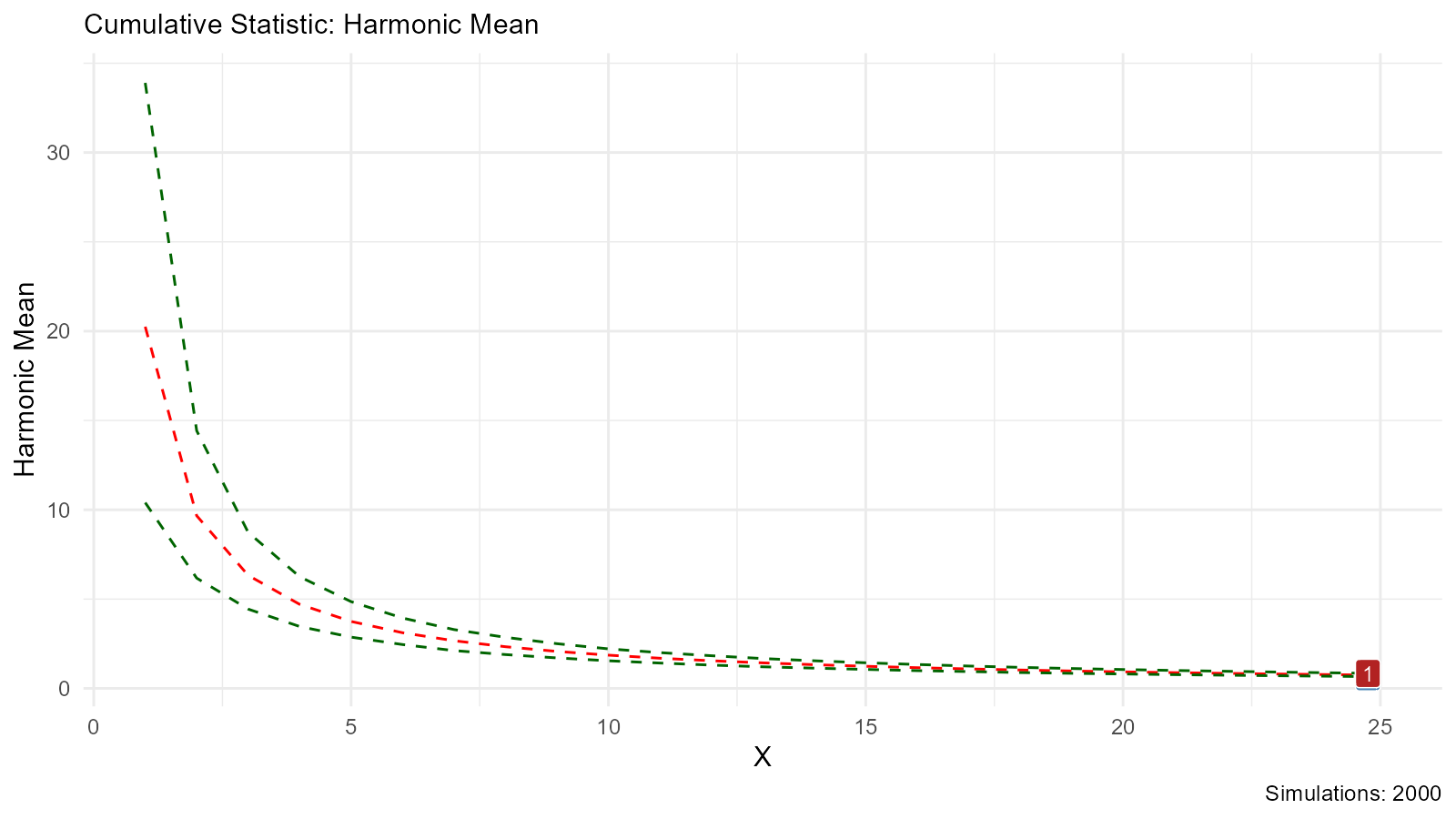
# Show Groups
bootstrap_stat_plot(bootstrap_data, .value = y, .stat = "cmean",
.show_groups = TRUE)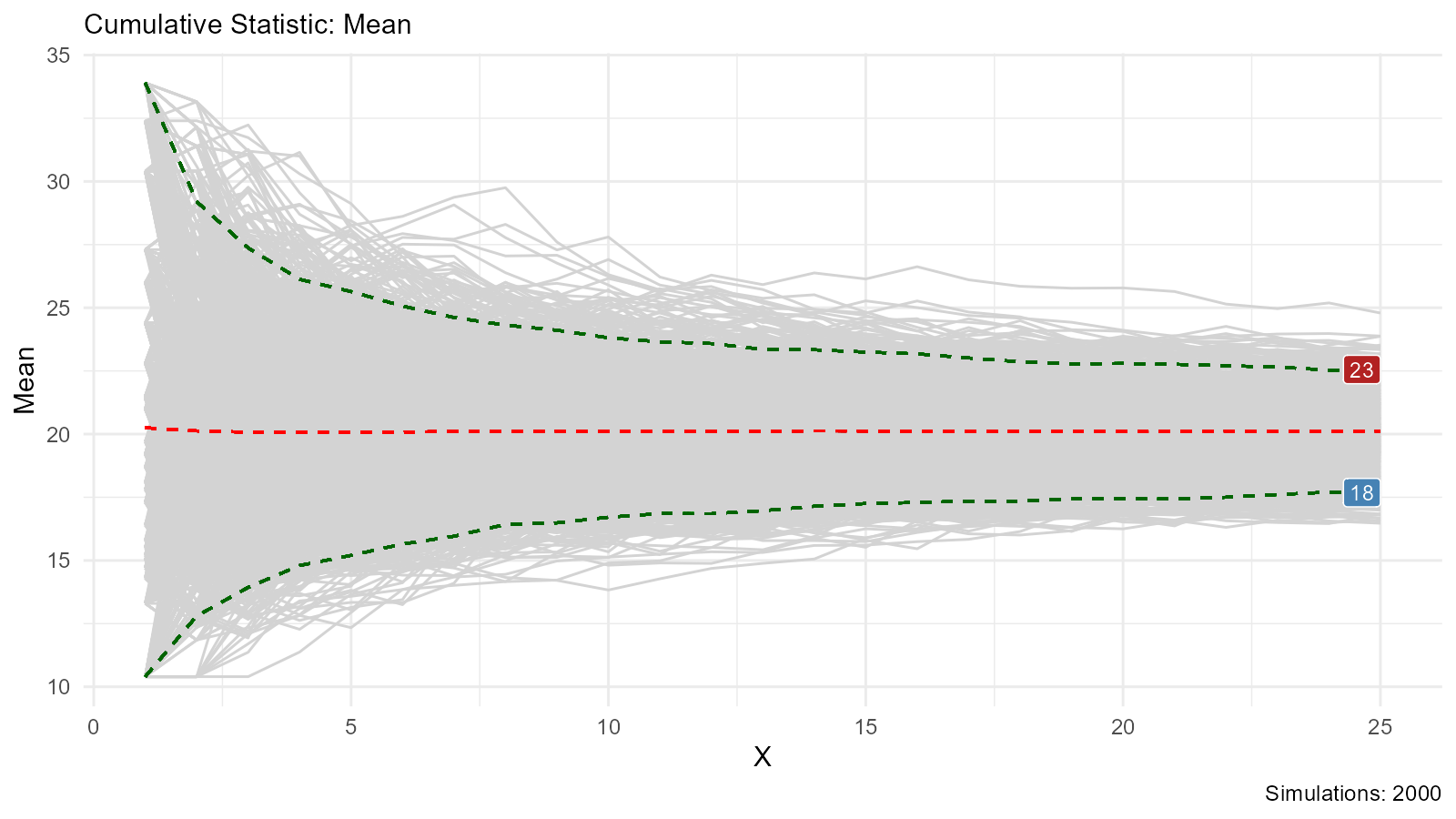
Quick Statistics
# Get basic statistics
summary(bootstrap_data |> bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |> pull(y))
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 10.40 15.50 19.20 20.12 22.80 33.90
# Count simulations
length(unique(bootstrap_data$sim_number))
#> [1] 2000Bootstrap Statistics
Unnesting Bootstrap Data
Use bootstrap_unnest_tbl() to work with bootstrap
samples:
# Unnest the bootstrap data
unnested <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl()
# Now you can calculate statistics
head(unnested)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 2
#> sim_number y
#> <fct> <dbl>
#> 1 1 15
#> 2 1 10.4
#> 3 1 30.4
#> 4 1 15.2
#> 5 1 22.8
#> 6 1 19.2Calculating Bootstrap Statistics
# Calculate statistics for each bootstrap sample
bootstrap_stats <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
group_by(sim_number) |>
summarise(
mean = mean(y),
median = median(y),
sd = sd(y),
q25 = quantile(y, 0.25),
q75 = quantile(y, 0.75)
)
# View distribution of means
summary(bootstrap_stats$mean)
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 16.47 19.34 20.09 20.12 20.91 24.79
hist(bootstrap_stats$mean, main = "Bootstrap Distribution of Mean",
xlab = "Mean", col = "lightblue")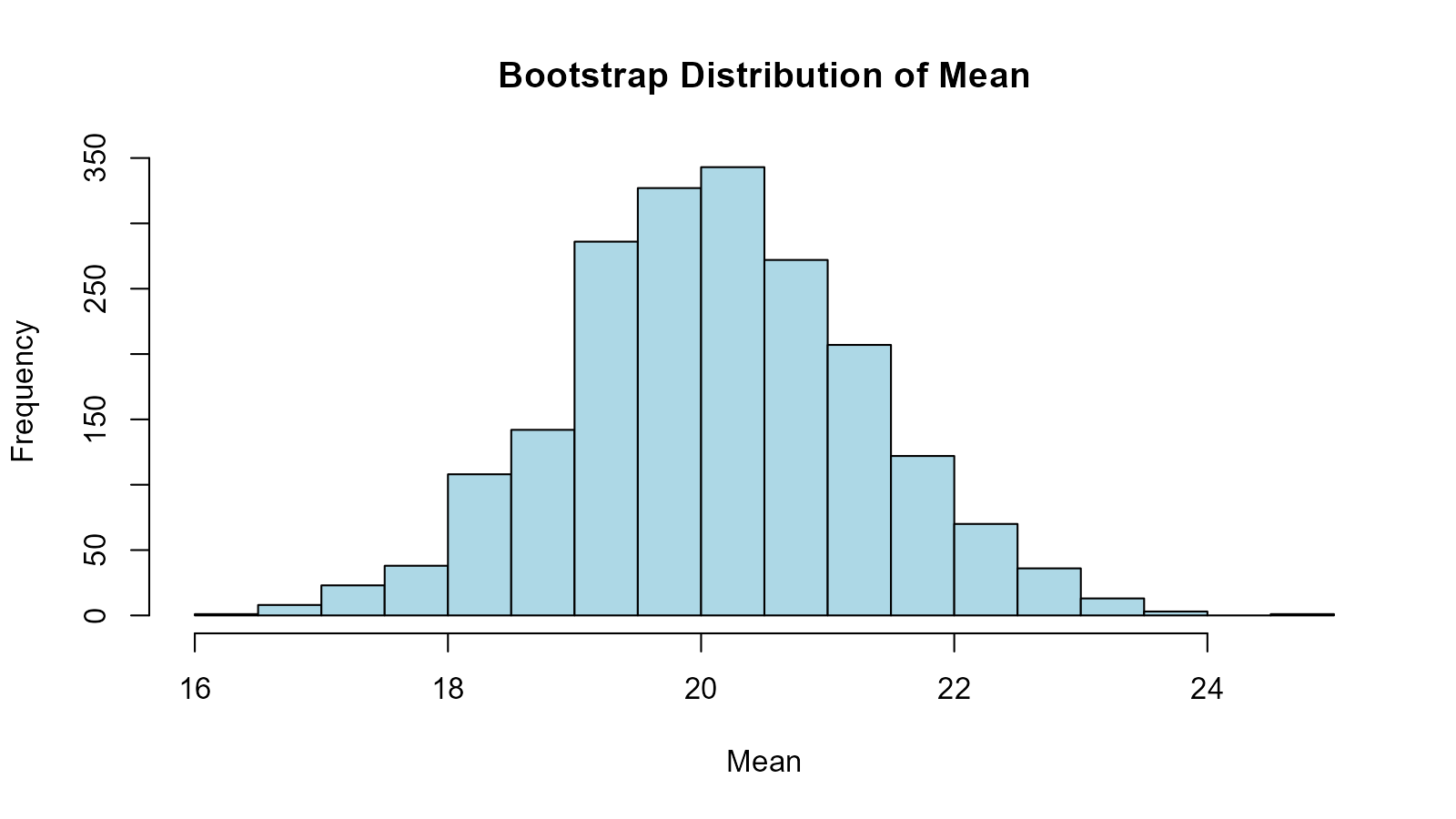
Overall Bootstrap Statistics
# Calculate overall statistics from all bootstrap samples
overall_stats <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
summarise(
mean_est = mean(y),
sd_est = sd(y),
median_est = median(y)
)
overall_stats
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> mean_est sd_est median_est
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 20.1 5.94 19.2Confidence Intervals
Bootstrap Percentile Method
Most common and intuitive method:
# Calculate 95% confidence intervals
ci_level <- 0.95
alpha <- 1 - ci_level
bootstrap_ci <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
summarise(
lower_ci = quantile(y, alpha/2),
upper_ci = quantile(y, 1 - alpha/2),
point_estimate = mean(y)
)
bootstrap_ci
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> lower_ci upper_ci point_estimate
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 10.4 33.9 20.1Confidence Intervals for Multiple Statistics
# Calculate CI for mean, median, and sd
ci_stats <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
group_by(sim_number) |>
summarise(
mean = mean(y),
median = median(y),
sd = sd(y)
) |>
summarise(
across(
c(mean, median, sd),
list(
lower = ~ unname(quantile(.x, 0.025)),
estimate = ~ unname(mean(.x)),
upper = ~ unname(quantile(.x, 0.975))
)
)
)
glimpse(ci_stats)
#> Rows: 1
#> Columns: 9
#> $ mean_lower <dbl> 17.6837
#> $ mean_estimate <dbl> 20.11925
#> $ mean_upper <dbl> 22.5564
#> $ median_lower <dbl> 16.4
#> $ median_estimate <dbl> 19.28125
#> $ median_upper <dbl> 21.4025
#> $ sd_lower <dbl> 4.104046
#> $ sd_estimate <dbl> 5.879158
#> $ sd_upper <dbl> 7.384673Visualizing Confidence Intervals
# Create visualization
unnested |>
ggplot(aes(x = y)) +
geom_density(fill = "lightblue", alpha = 0.5) +
geom_vline(xintercept = unname(quantile(unnested$y, 0.025)),
linetype = "dashed", color = "red") +
geom_vline(xintercept = unname(quantile(unnested$y, 0.975)),
linetype = "dashed", color = "red") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(unnested$y),
linetype = "solid", color = "darkblue", linewidth = 1) +
labs(
title = "Bootstrap Distribution with 95% CI",
x = "Bootstrap Statistic",
y = "Density"
) +
theme_minimal()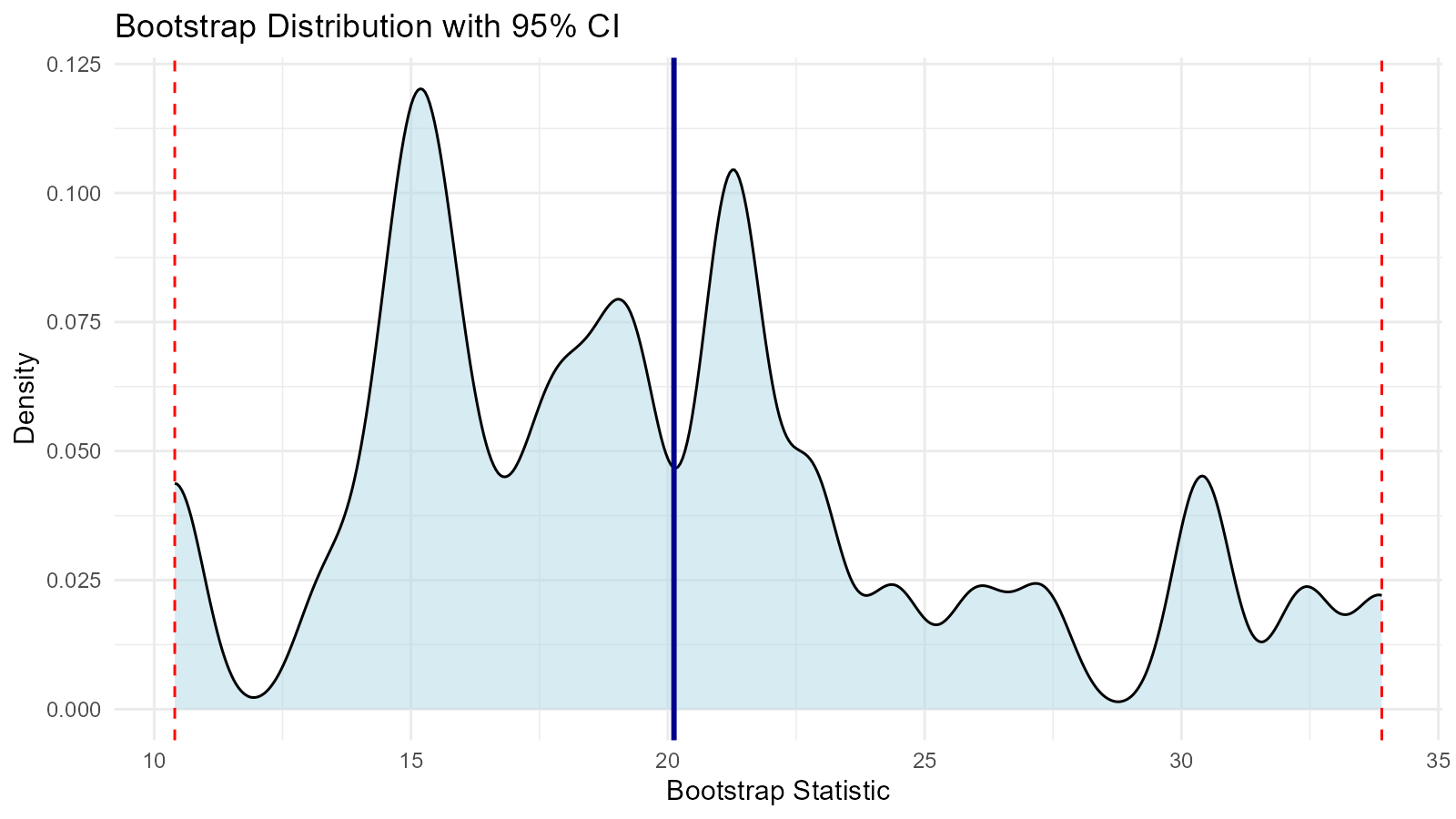
Bootstrap Augmentation Functions
Augment Density
Add density calculations to bootstrap data:
# Augment with density information
augmented_density <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_density_augment()
head(augmented_density)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> sim_number x y dx dy
#> <fct> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 1 15 1.30 0.0000593
#> 2 1 2 10.4 3.04 0.000286
#> 3 1 3 30.4 4.78 0.00102
#> 4 1 4 15.2 6.51 0.00279
#> 5 1 5 22.8 8.25 0.00624
#> 6 1 6 19.2 9.99 0.0124Augment Probability
Add cumulative probability:
# Augment with probability information
augmented_prob <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
bootstrap_p_augment(y)
head(augmented_prob)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> sim_number y p
#> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 15 0.186
#> 2 1 10.4 0.0618
#> 3 1 30.4 0.937
#> 4 1 15.2 0.249
#> 5 1 22.8 0.779
#> 6 1 19.2 0.530Augment Quantile
Add quantile information:
# Augment with quantile information
augmented_quantile <- bootstrap_data |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
bootstrap_q_augment(y)
head(augmented_quantile)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 3
#> sim_number y q
#> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 15 10.4
#> 2 1 10.4 10.4
#> 3 1 30.4 10.4
#> 4 1 15.2 10.4
#> 5 1 22.8 10.4
#> 6 1 19.2 10.4Advanced Bootstrap Techniques
Bootstrap for Difference of Means
# Two groups
group1 <- mtcars$mpg[mtcars$am == 0]
group2 <- mtcars$mpg[mtcars$am == 1]
# Bootstrap function for difference
bootstrap_diff <- function(n_sims = 2000) {
diffs <- numeric(n_sims)
for (i in 1:n_sims) {
boot_g1 <- sample(group1, length(group1), replace = TRUE)
boot_g2 <- sample(group2, length(group2), replace = TRUE)
diffs[i] <- mean(boot_g2) - mean(boot_g1)
}
return(diffs)
}
# Run bootstrap
diff_dist <- bootstrap_diff(2000)
# Calculate CI
quantile(diff_dist, c(0.025, 0.975))
#> 2.5% 97.5%
#> 3.827439 10.924939
# Visualize
hist(diff_dist, main = "Bootstrap Distribution of Difference in Means",
xlab = "Difference in Means", breaks = 50, col = "lightgreen")
abline(v = quantile(diff_dist, c(0.025, 0.975)),
col = "red", lty = 2, lwd = 2)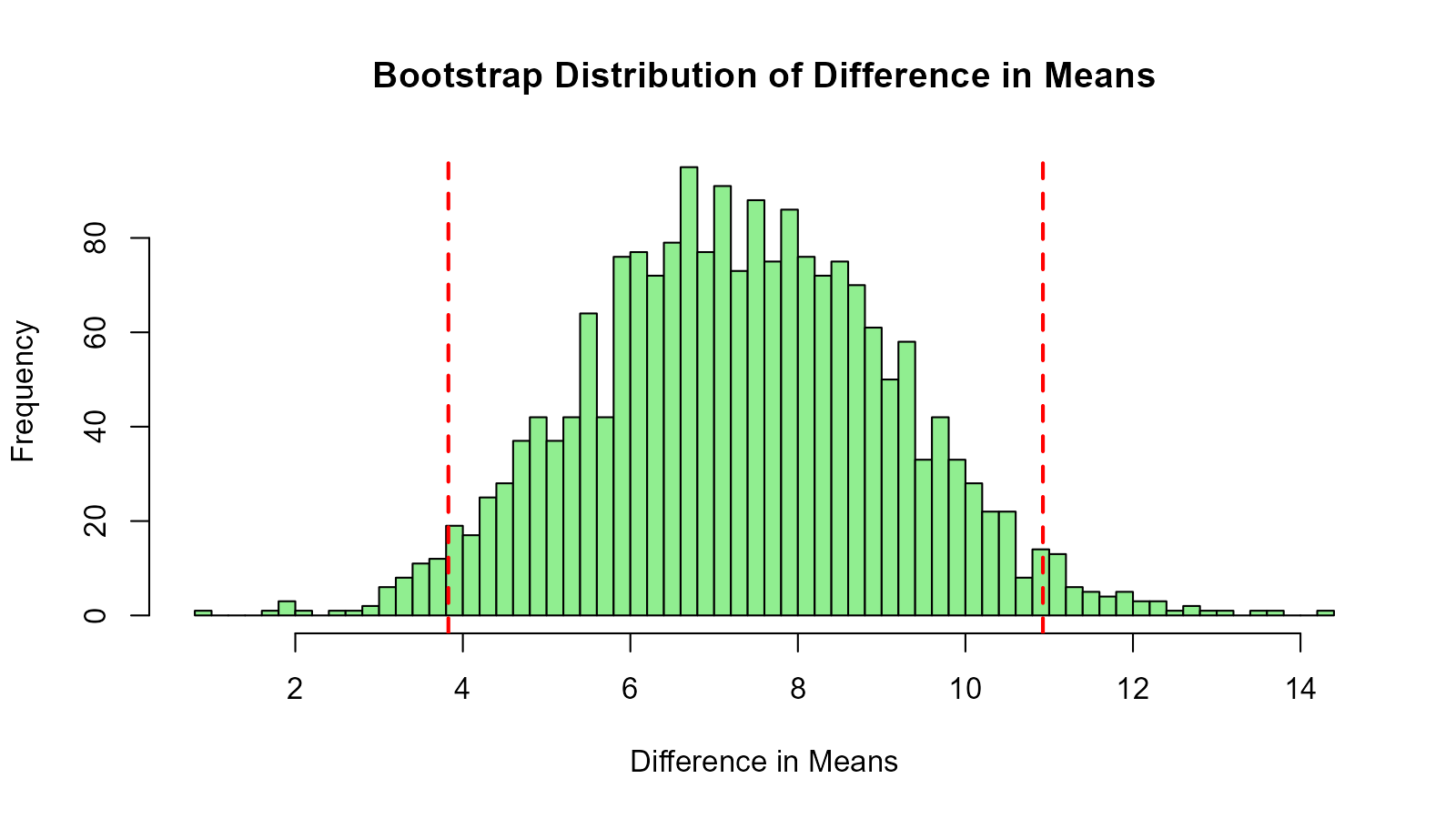
Bootstrap for Correlation
# Original correlation
cor_original <- cor(mtcars$mpg, mtcars$wt)
# Bootstrap correlations
boot_cor <- function(x, y, n_sims = 2000) {
cors <- numeric(n_sims)
n <- length(x)
for (i in 1:n_sims) {
indices <- sample(n, replace = TRUE)
cors[i] <- cor(x[indices], y[indices])
}
return(cors)
}
# Run bootstrap
cor_dist <- boot_cor(mtcars$mpg, mtcars$wt, 2000)
# CI for correlation
cor_ci <- quantile(cor_dist, c(0.025, 0.975))
cat("95% CI for correlation:", cor_ci, "\n")
#> 95% CI for correlation: -0.9276411 -0.7921946
# Visualize
hist(cor_dist, main = "Bootstrap Distribution of Correlation",
xlab = "Correlation Coefficient", breaks = 50, col = "lightyellow")
abline(v = cor_ci, col = "red", lty = 2, lwd = 2)
abline(v = cor_original, col = "blue", lwd = 2)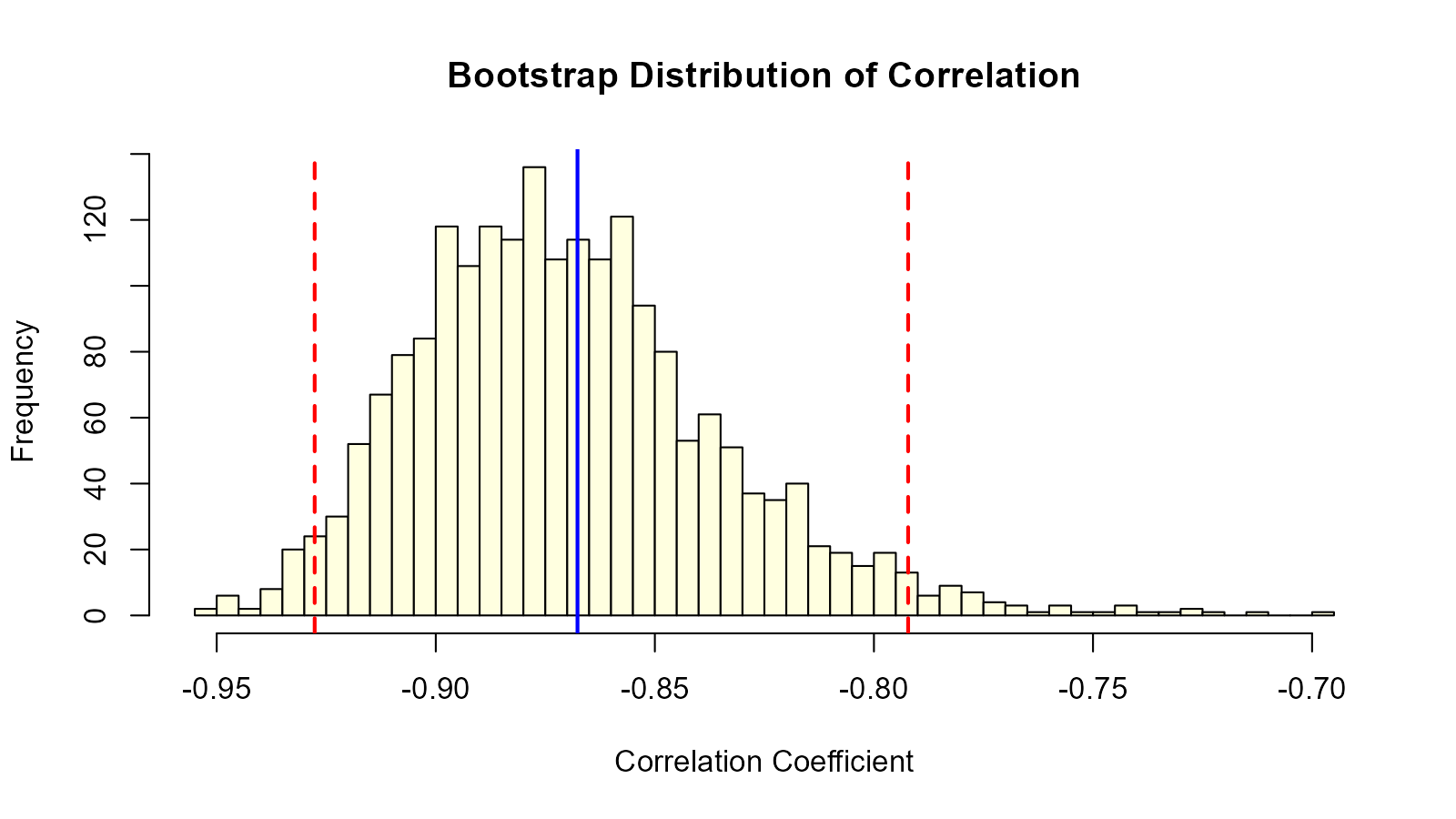
Visualization
Multiple Visualizations
# Generate bootstrap data
boot_data <- tidy_bootstrap(mtcars$mpg, .num_sims = 2000) |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl()
# Create multiple plots
p1 <- ggplot(aes(x = y), data = boot_data) +
geom_density(fill = "lightgreen", alpha = 0.5) +
labs(title = "Density Plot", x = "Value", y = "Density") +
theme_minimal()
p2 <- ggplot(aes(x = y), data = boot_data) +
stat_ecdf(aes(x = y), geom = "step", color = "blue") +
labs(title = "Probability Plot", x = "Value", y = "Cumulative Probability") +
theme_minimal()
p3 <- ggplot(aes(x = seq_along(y), y = sort(y)), data = boot_data) +
geom_point(color = "purple", alpha = 0.1) +
labs(title = "Sorted Values", x = "Index", y = "Value") +
theme_minimal()
p4 <- ggplot(aes(sample = y), data = boot_data) +
stat_qq(color = "orange", alpha = 0.1) +
stat_qq_line(color = "red") +
labs(title = "QQ Plot", x = "Theoretical Quantiles", y = "Sample Quantiles") +
theme_minimal()
# Combine
(p1 | p2) / (p3 | p4)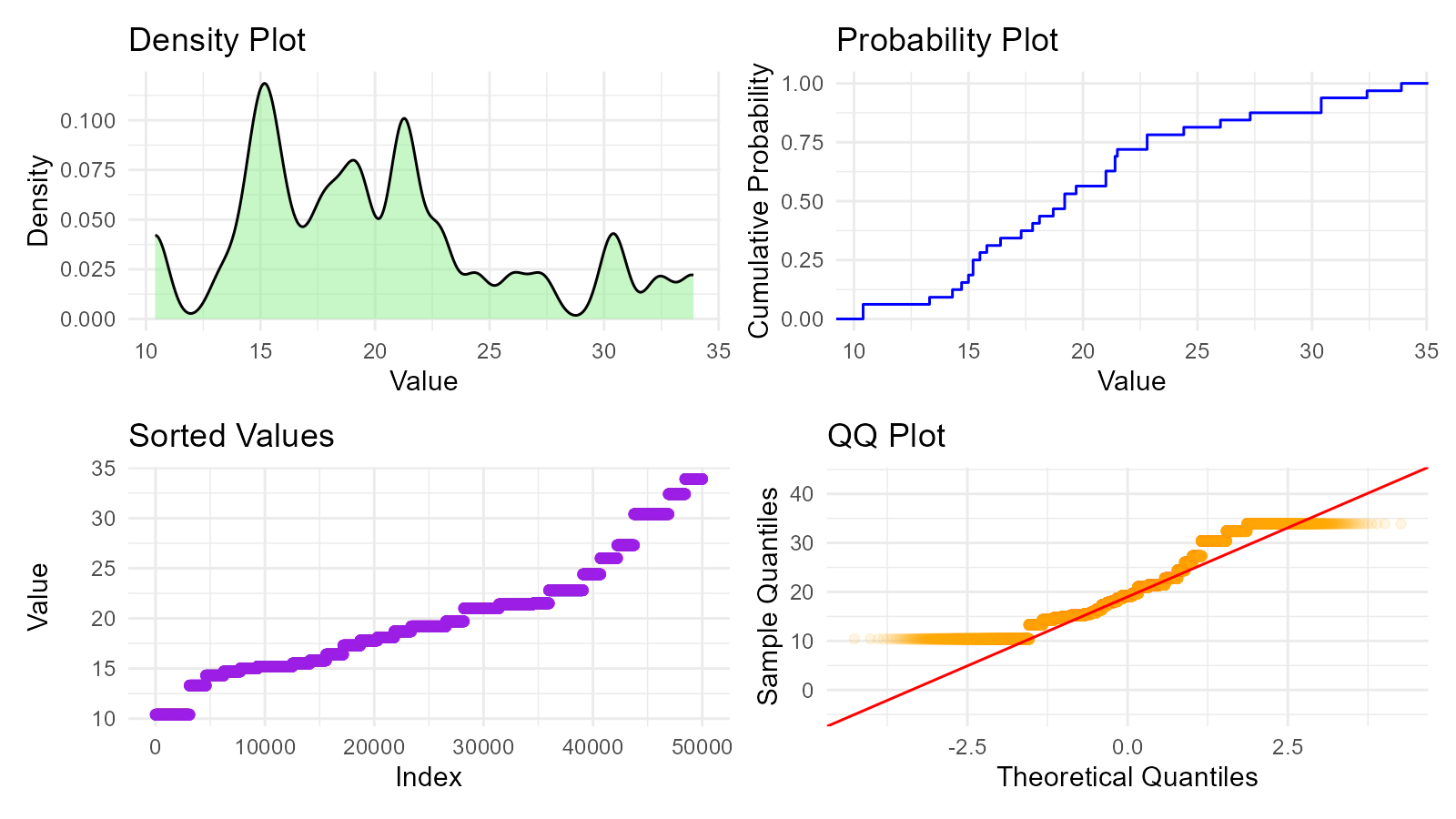
Custom Visualization with CI
# Calculate statistics
ci <- quantile(boot_data$y, c(0.025, 0.5, 0.975))
# Create plot
ggplot(data.frame(y = boot_data$y), aes(x = y)) +
geom_density(fill = "skyblue", alpha = 0.5) +
geom_vline(xintercept = ci[1], linetype = "dashed", color = "red") +
geom_vline(xintercept = ci[2], linetype = "solid", color = "darkblue",
linewidth = 1.5) +
geom_vline(xintercept = ci[3], linetype = "dashed", color = "red") +
annotate("text", x = ci[1], y = 0, label = "2.5%", vjust = -1) +
annotate("text", x = ci[2], y = 0, label = "Median", vjust = -1) +
annotate("text", x = ci[3], y = 0, label = "97.5%", vjust = -1) +
labs(
title = "Bootstrap Distribution with Confidence Interval",
x = "Statistic Value",
y = "Density"
) +
theme_minimal()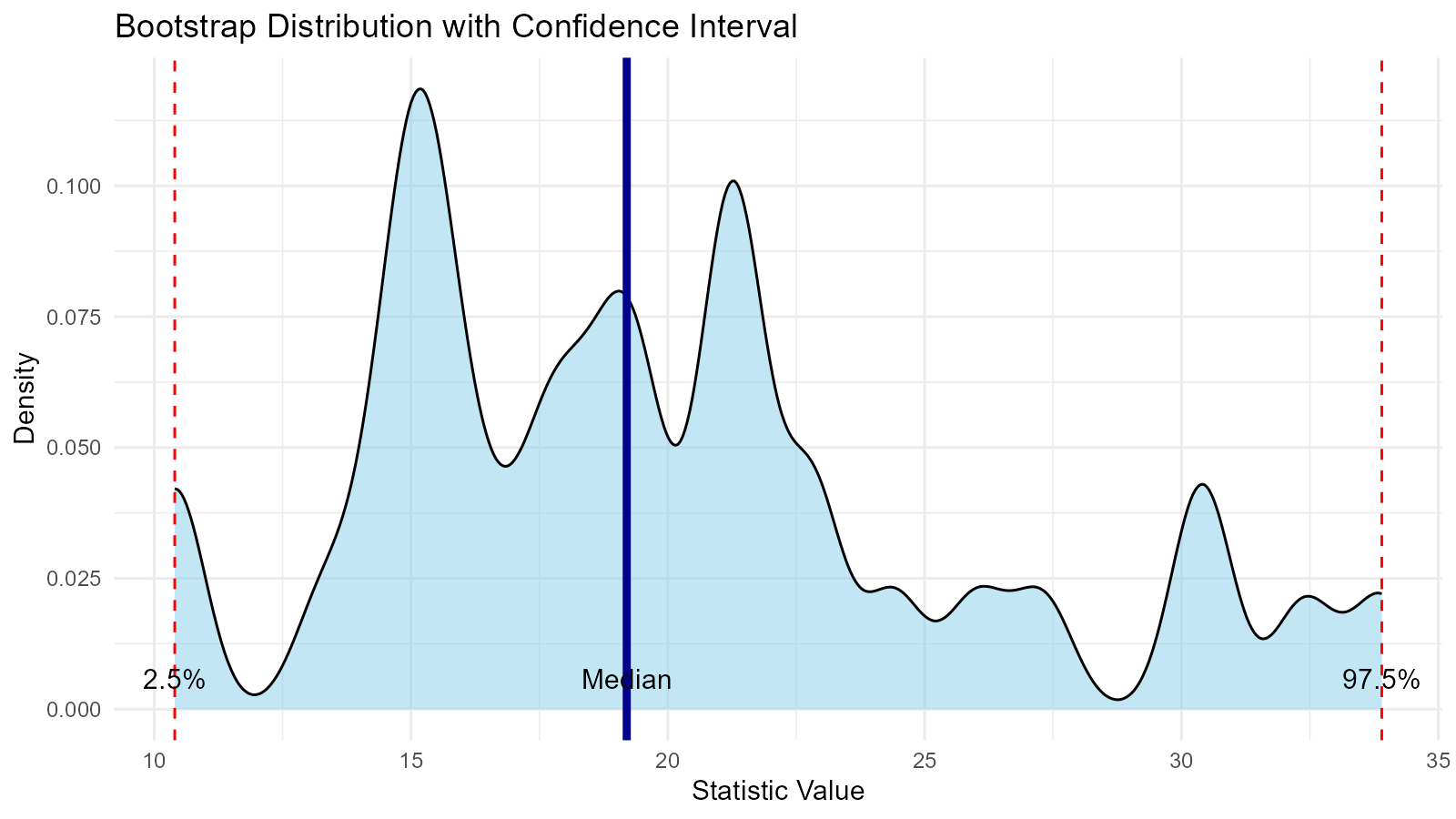
Best Practices
1. Choose Appropriate Number of Simulations
General guidelines:
- Exploratory: 1000 simulations
- Standard analysis: 2000-5000 simulations
- Publication/Critical: 10000+ simulations
2. Verify Bootstrap Convergence
Check stability with different numbers of simulations:
# Check stability with different numbers of simulations
n_sims_vec <- c(500, 1000, 2000)
convergence <- data.frame(
n_sims = n_sims_vec,
mean_est = NA,
ci_lower = NA,
ci_upper = NA
)
for (i in seq_along(n_sims_vec)) {
boot <- tidy_bootstrap(data, .num_sims = n_sims_vec[i])
stats <- boot |>
bootstrap_unnest_tbl() |>
summarise(
mean = mean(y),
lower = quantile(y, 0.025),
upper = quantile(y, 0.975)
)
convergence[i, 2:4] <- as.numeric(stats)
}
convergence
#> n_sims mean_est ci_lower ci_upper
#> 1 500 20.11131 10.4 33.9
#> 2 1000 20.06232 10.4 33.9
#> 3 2000 20.07139 10.4 33.9